Data Analyst vs. Scientist: Key Differences
Table of Contents
Confused between data scientist and data analyst roles? Learn the key differences in skills, tools, salary, and career paths in this simple, beginner-friendly guide.
Why This Comparison Matters
Let us start with something easy. If you want to work with data, you need to understand how different roles work. The most popular are Data Analyst and Data Scientist. The fastest-growing professions are Data Analyst and Data Scientist. Both have to do work on the data, but what you do daily, the tools you use, and how you develop in your career will change greatly.
Understanding these differences will not only save you time but also help you in selecting the career that best suits your background and interests.
Before you go, pause for a while and think about: Do you like solving technical challenges and writing code? Or do you like analyzing reports, making dashboards, and explaining what the data means?
What is a Data Analyst?
A data analyst is a person who analyzes the data that may be sales and website visits or the customer feedback with that certain data, the company can understand what those numbers actually mean and why they matters?
For example:
If a company wants to know “Why did sales drop last month?”, a data analyst will check the numbers and create a report that shows:
Sales dropped more in a certain region
Most people stopped buying after a price increase
One product was returned more often than others
They don’t just look at numbers—they find the story behind the numbers and help the company take the right action.
If you’re comfortable with numbers and love making clear reports, data analytics is a great start.
Skills Required
You’ll need:
- Microsoft Excel
- SQL
- Descriptive statistics
- Data visualization tools
- Clear communication
Tools They Use
Common tools include
- Power BI
- Google Sheets
- Tableau
- Excel
- MySQL
What is a Data Scientist?
A data scientist is someone who works with a lot of messy or raw data to find useful patterns and make predictions. They don’t just look at the data—they actually build smart systems (using machine learning) that can learn from that data. For example, using tools like Python, Jupyter Notebook, or even AI libraries like TensorFlow, a data scientist can help predict things like which products customers might buy next.
Real-Life Example
Let’s say you’re working at an online Shopping company. Your manager says,
“Can we figure out which customers might stop buying from us soon?”
Now, that’s not something you can figure out just by looking at numbers in a table.
This is where a data scientist comes in.
They’ll collect all kinds of data — like how often people shop, what they usually buy, how long they’ve been inactive, and even if they returned products.
Then they’ll use tools like Python, Jupyter Notebook, or TensorFlow (which is just a library that helps build smart models) to train a system that learns from past data. Once trained, this system can say,
“Hey, these 500 customers are showing signs they might stop shopping soon.”
Now the company can do something about it — maybe send discounts or personalized emails — before losing those customers.
Skills Required
To succeed as a data scientist, you’ll need:
- Programming (Python, R)
- Machine learning algorithms
- Advanced statistics
- Data wrangling
- Visualization
Tools They Use
Popular tools include:
- Jupyter Notebook
- Scikit-learn
- TensorFlow
- SQL
- Tableau
Most data scientists start as analysts or come from coding/maths backgrounds.
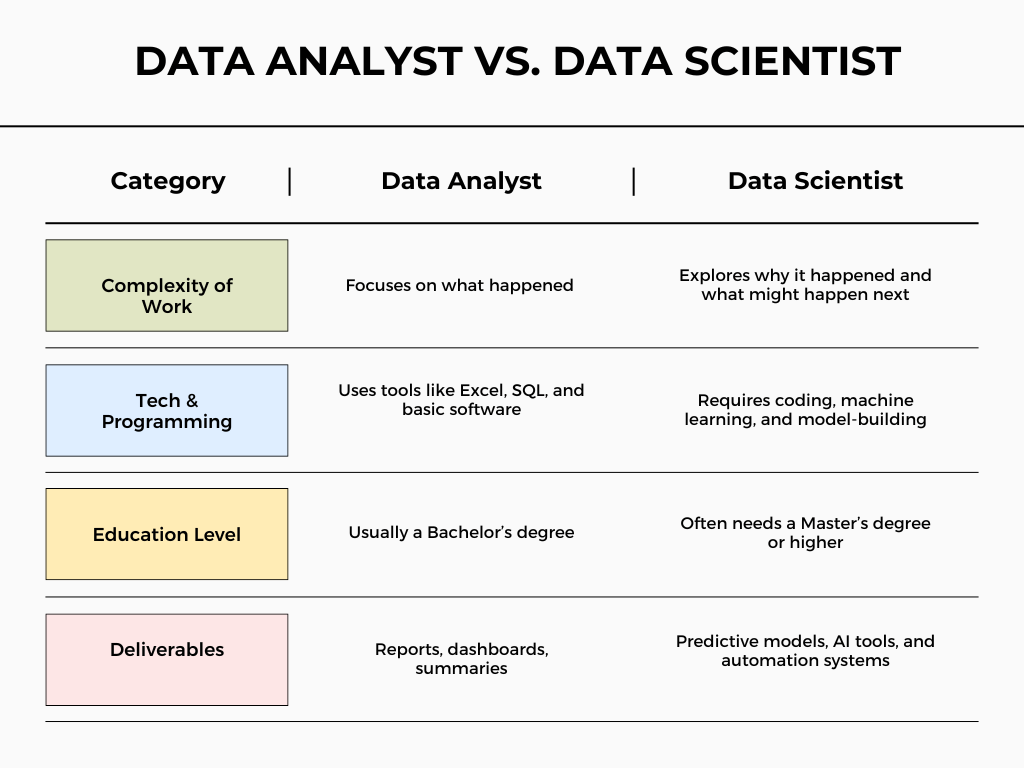
Key Differences
What Should You Study?
When considering a job as a data analyst or scientist, one common question is, “What should I study to get there?”.
Let’s break it down clearly for both paths so you know where to begin.
For Data Analysts (If You Want to Start Quickly and Grow Gradually)
If you want to get started in the data field fast, becoming a data analyst is excellent. It is more beginner-friendly, focusing on business understanding, numbers, and visualizations.
Formal Degrees
BBA or BSc in Business Analytics
These programs combine business thinking with technical tools. You’ll learn how to use data to support business decisions.
Economics or Statistics
Helpful for roles in finance, research, or reporting-heavy jobs.
Short-Term Courses & Certifications (Build the Right Foundation)
If you’re beginning to work with data, you don’t need to explore into complicated programming right away. There are short-term courses directed primarily for beginners that will give you the practical skills required for a data analyst position.
Google Data Analytics Certificate (via Coursera)
This is one of the most beginner-friendly programs out there. It walks you through data cleaning, Excel basics, SQL, Tableau, and even how to approach problems like a real analyst — no prior experience needed.
Excel & SQL Training
These two are must-haves for any data analyst. While there are many ways to learn them, going through a structured program at a trusted institute like Whitescholars Academy can make a big difference. Instead of wasting time on random videos, you’ll follow a proper step-by-step curriculum, get real support, and actually understand how these tools are used in real companies.
Power BI or Tableau Courses
Learning how to develop clean, easy-to-understand dashboards is a key component of becoming an analyst. Whitescholars will provide you with practical training on products such as Power BI, helping you to show data in a way that tells a clear story.
For Data Scientists (If You Want to Go Deeper with Data and AI)
If you’re someone who enjoys solving problems, working with data, and you’re curious about how machines can “learn” from patterns — then becoming a data scientist might be your ideal path.
Now, this role needs an advanced technical background, especially in math, statistics, and programming. But don’t worry—with proper training, anyone with an interest and dedication can learn these skills.
Formal Degrees That Help
BSc or MSc in Computer Science
A great foundation for coding, algorithms, and understanding how data systems work.
Statistics or Mathematics
These subjects help you work with real data — understanding patterns, probabilities, and models.
Engineering (IT, Computer, or AI branch)
Especially useful if you enjoy building systems or tools that solve real-world problems.
Specialized Certifications & Practical Training
While a degree is helpful, many people enter data science through focused learning programs. Instead of bouncing between online videos, it’s much better to follow a proper structure.
That’s where a trusted institute like Whitescholars Academy can make a huge difference.
At Whitescholars Academy, you’ll get:
Step-by-step training in Python, machine learning, and real-life case studies
Guidance on how to actually build and deploy predictive models
Support from trainers when you get stuck — something videos can’t offer
real projects that prepare you for the kind of work companies expect
Whether it’s a bootcamp or a longer certification, going through a structured learning journey with mentorship saves time and builds real confidence.
What You’ll Learn Along the Way
By enrolling in a proper data science program, you’ll learn:
Python or R programming (used to process and analyze data)
Data cleaning and preparation (making raw data ready for use)
Machine learning basics like regression, classification, and clustering
How to use tools like TensorFlow and Scikit-learn to build smart models
How to test your models and make them better over time
You don’t need a Master’s degree to get started — but going deep with the help of a reliable academy like Whitescholars can fast-track your career and help you move into advanced roles more confidently.
Career Journey & Growth Paths
Every career has a beginning, middle, and advanced stage. Here’s what yours could look like.
Entry-Level Jobs
Data Analyst
Business Intelligence Analyst
Data Science Intern
Mid-Level Roles
Data Engineer
Machine Learning Engineer
Senior Analyst
Senior Roles
Data Science Manager
Chief Data Officer
Analytics Head
Path Planning Tip: Your journey doesn’t end with one role. Upskill regularly to grow in this field.
Conclusion
So, what is the end takeaway?
If you are good with numerals, creating charts, and clearly expressing ideas being a data analyst could be a great fit. It’s a good way to get into the world of data without having to code too much.
However, if you are curious about how things work behind the scenes, like handling complex problems, and are willing to learn coding and machine learning, becoming a data scientist might be a better fit.
What is the good news? You don’t need to figure everything out right away. Many people begin their careers as analysts before transitioning to data science. Simply start learning one step at a time.
FAQ’s
1. Can I become a data analyst without a technical background?
Yes, you can. Many data analysts come from business, commerce, or even arts backgrounds. Start with Excel, SQL, and visualization tools like Power BI.
2. Is coding necessary for data analytics?
Not in the beginning. You can do most analyst tasks using tools like Excel, SQL, and dashboard software. But learning Python later will definitely help you grow.
3. Do I need a Master’s degree to become a data scientist?
No, it’s not mandatory. While a Master’s can help, many data scientists learn through bootcamps, online certifications, or practical project-based courses from institutes like Whitescholars Academy.
4. How long does it take to become a data analyst or data scientist?
If you’re consistent, you can learn the basics of data analysis in 3–6 months. Data science might take 6–12 months or more, depending on how deep you go and how much time you invest.
5. Which one pays more — data analyst or data scientist?
Generally, data scientists earn more because their work involves advanced skills like machine learning. But salaries also depend on your experience, location, and the company you work for.
