Data Science in 2026: Essential Tools & Skills for Success

Table of Contents
Master the data science landscape in 2026. Discover the must-have libraries, tools, and lucrative skills needed to launch a successful career today.
The State of Modern Data Science
As machine learning algorithms develop and datasets become more complex, the data science ecosystem is growing quickly. Over 400 million terabytes of data are currently produced every day, and this amount is expected to increase as social media and video consumption soar.
In order to manage statistical models and predictive analytics at scale, modern organizations now rely on complex pipelines like Apache Spark. Data science is now a key component of contemporary business strategy, and this growth is also being fueled by the growing digitization of traditional industries.
Essential Libraries And Platforms
Fundamental Libraries for Numerical Power
The fundamental, pre-built functions required for data manipulation and machine learning are provided by programming libraries. Because of its extensive ecosystem for numerical computing, Python continues to be the most popular language. Key libraries consist of
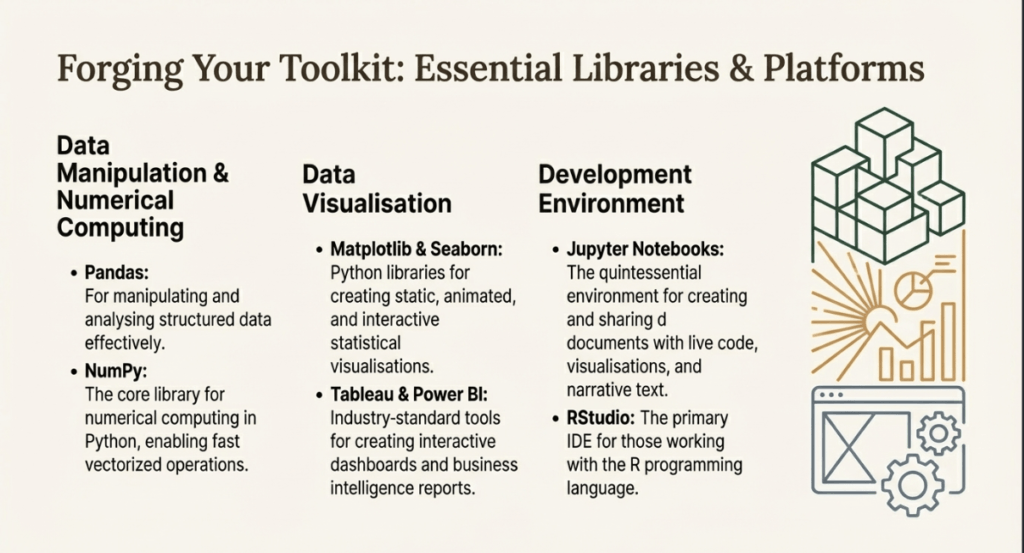
- For handling structured data and carrying out quick numerical operations, Pandas and NumPy are crucial.
- Scikit-learn: A comprehensive library with more than 150 clustering, regression, and classification algorithms.
- The top options for deep learning and neural network development are TensorFlow and PyTorch.
- R Tidyverse: A group of packages that offer a standardized syntax for statistical research and modeling. As a high-performance substitute for Pandas for users working with extraordinarily large datasets that demand quicker processing times, Polars is becoming increasingly popular.
High-Performance Platforms for Data Investigation
Finding patterns and running statistical tests to inform business decisions are expedited by analytical tools.
- Jupyter Notebooks: These enable the combination of code and visualizations in more than 40 languages, creating a “living” computing environment.
- Enterprise Solutions: High-level statistical processing is made possible by programs like SAS and SPSS, which frequently have intuitive user interfaces and don’t require a lot of programming.
- Cloud Platforms: Databricks facilitates collaborative work across Python, R, and SQL and combines machine learning with data engineering. It is based on Apache Spark.
- Many people now prefer Visual Studio Code (VS Code) over other integrated development environments (IDEs) because its Jupyter extension makes professional software development more efficient than using traditional browser-based notebooks.
Advanced Utilities for Visual Communication
For both technical and non-technical stakeholders, visualization tools convert intricate numerical results into interactive dashboards.
- Business Intelligence (BI) Tools: Tableau and Power BI are industry leaders, enabling natural language queries and drag-and-drop dashboard creation.
- Programmatic Libraries: ggplot2 benefits the R community, while Matplotlib and Seaborn provide exact control over visual layouts in Python.
- Web-Based Graphics: Interactive, web-ready visualizations with features like zooming and filtering are made possible by Plotly and D3.js. Additionally, start investigating Streamlit, an open-source Python library that eliminates the need for front-end development skills by enabling data scientists to create shareable web apps from data scripts in a matter of minutes.
Intelligence-Driven Tools Reshaping the Field
Previously labor-intensive and manual processes like feature engineering and model selection are now being automated by AI-driven tools.
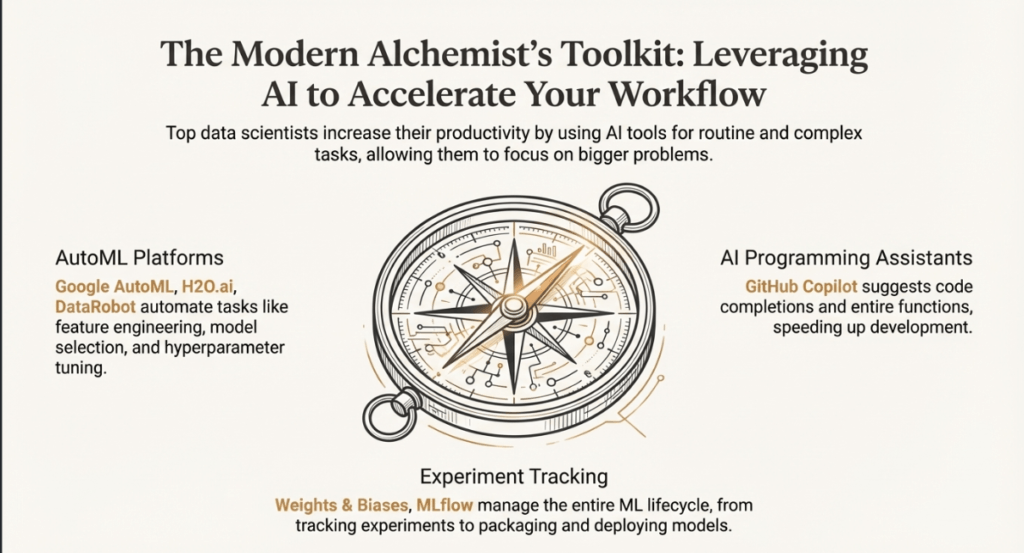
- AutoML Platforms: Google AutoML, H2O.ai, and DataRobot aid in the rapid construction of high-accuracy models, sometimes cutting development times from months to days.
- GitHub Coding Assistants Copilot greatly increases productivity by using AI to recommend functions and code completions.
- Experiment tracking: To guarantee reproducibility in team-based projects, tools like MLflow and Weights & Biases record parameters and metrics. These days, data workflows directly incorporate Large Language Models (LLMs) to help explain code, create synthetic data for testing, and even carry out preliminary data cleaning using natural language commands.
Optimizing Efficiency by Harmonizing Technical Ecosystems
To reduce errors and do away with manual data transfers across platforms, integration is essential. Standardized APIs are used in modern workflows to connect deployment systems and programming environments.
These pipelines can be managed by programs like Apache Airflow, which automatically initiates model retraining upon the detection of fresh data. In order to keep track of modifications and promote teamwork, version control is also crucial.
The Human Element: Strategy and Domain Context
A data scientist’s main goal is to solve business problems, even though technical tools are essential. This needs:
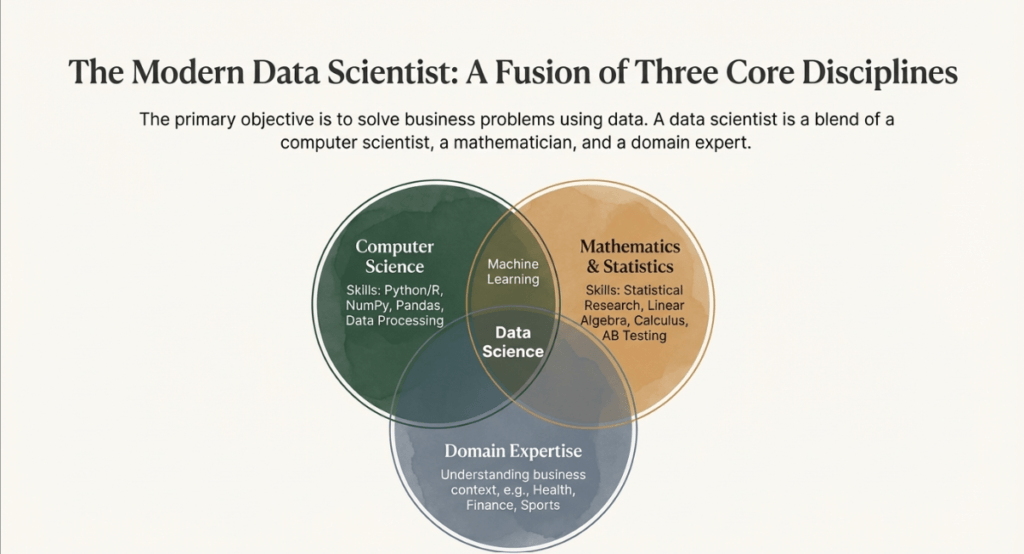
- Domain Expertise: To offer insightful commentary, you must have a thorough understanding of the particular industry, be it healthcare, sports, or finance.
- Communication: You need to be able to explain technical results to stakeholders who might not have a technical background.
- Problem Identification: The capacity to define a problem with leadership (such as a CEO) prior to data sourcing and cleaning.
The Strategic Mission and Workflow of the Modern Data Scientist
The Objective: Driving Business Solutions with Data
A data scientist’s main goal is to solve complicated business issues by deriving valuable insights from unstructured, raw data. A data scientist’s job is to find hidden patterns and offer useful insights that stakeholders can use to create better products or enhance decision-making because data is essentially “meaningless” until it is processed. They essentially serve as a link between corporate strategy and unprocessed data.
Basic Data Manipulation Toolkits
Data scientists use core data science libraries like Pandas and NumPy to manipulate structured data and carry out numerical calculations in order to fulfill their duties. During the modeling stage, libraries like Scikit-learn offer more than 150 algorithms for tasks like regression and classification, while TensorFlow and PyTorch are utilized for neural networks and deep learning.
Advanced Platforms for Statistical Investigation
Data scientists use cutting-edge data analysis tools outside of libraries to speed up data exploration. For the creation of dynamic documents that integrate code and visualizations, Jupyter Notebooks are crucial.
Tools like SAS and SPSS provide point-and-click interfaces for complex statistical processing without requiring extensive programming for users in enterprise settings. With the help of these platforms, data scientists can conduct Exploratory Data Analysis (EDA) to determine which variables will be most helpful for their models.
Communicating Insights through Visual Clarity
Working and interacting with non-technical stakeholders is a crucial duty. Top data visualization tools like Tableau and Power BI can be used to create interactive dashboards with drag-and-drop interfaces.
For research-quality figures, programmatic libraries like Matplotlib and Seaborn provide more precise control. This is an essential step because a data scientist needs to be able to communicate technical results in a way that non-technical people can comprehend.
The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Development
AI tools that automate repetitive tasks like feature engineering and parameter tuning are revolutionizing the role. AutoML platforms such as Google AutoML and DataRobot can reduce model development times from months to days. Additionally, data scientists can concentrate on higher-level problem solving rather than syntax thanks to AI coding assistants like GitHub Copilot, which recommend entire functions.
The data scientist is still in charge of ethically monitoring these automated models to make sure they don’t reinforce biases in the training data, even though these tools boost productivity.
Simplifying the Lifecycle of Data Science
A workflow must incorporate tools to minimize errors and do away with manual data transfers in order to be effective. This entails utilizing tools like Apache Airflow to manage pipelines and utilizing APIs to connect databases with analytical platforms. When new data is found, these systems can automatically initiate model retraining, guaranteeing that predictions hold true over time.
The Human Factor: Strategy and Domain Context
The requirement for domain expertise is a crucial duty that is frequently disregarded. In order to determine which questions to ask and which data is pertinent, a data scientist must be knowledgeable about the particular industry, whether they work in healthcare, sports, or finance. Before any data is even gathered, they must collaborate closely with leadership (such as a CEO) to define the problem statement.
AI tools for data science automation.
AI-driven tools have significantly transformed the data science landscape by automating intricate processes that were historically manual and time-consuming, such as feature engineering, model selection, and parameter tuning. By reducing the human effort required for routine analytical tasks, these tools allow professionals to focus on solving broader, more complex business problems.
Several important technologies are used to automate certain data science tasks:
1. Automated Machine Learning (AutoML)
The goal of AutoML platforms is to simplify the entire machine learning model development process:
- Feature Engineering and Model Building: To achieve high accuracy in tasks like image classification, tools such as Google AutoML create custom models without the need for manual feature engineering.
- Algorithm Selection and Hyperparameter Tuning: H2O.ai facilitates distributed computing by automatically determining the best algorithms and hyperparameters for a given dataset.
- Quick Development and Deployment: DataRobot can cut the overall development time from months to just a few days by automating model deployment and monitoring.
2. Assistance with Code Generation and Analysis
Data scientists can now write code and explore data more effectively with the aid of AI tools that function as digital assistants:
- Coding Assistants: GitHub Copilot serves as an AI programming assistant by suggesting code completions and even entire functions based on the context of the work.
- Automated Insights: Certain tools, such as Perplexity Labs, can perform analysis automatically when a user uploads content. Additionally, AI can “spit out code” that can be directly integrated into tools to build projects, though beginners are advised to learn fundamentals first to understand the underlying logic.
3. Enhanced Visualisation and Natural Language Processing
Automation has also reached the “presentation” layer of data science:
- Smart Recommendations: Modern visualisation systems include intelligence capabilities that recommend the most appropriate chart types based on data attributes and the specific goals of the analysis.
- Natural Language Queries: By merely posing natural language queries, platforms such as Power BI enable users to automatically create visualizations, increasing the accessibility of data exploration.
4. Workflow Integration and Experiment Tracking
The dependability of data models is maintained by AI-driven cloud services and management platforms:
- End-to-End Managed Services: AWS SageMaker provides automatic scaling to meet various computational requirements and automates everything from data labeling to model deployment.
- Reproducibility and Tracking: Two tools that automate the recording of parameters, metrics, and training progress are Weights & Biases and MLflow. Collaboration and the replication of research depend on this.
- Automated Pipeline Triggers: Tools like Apache Airflow, which identify new data in a pipeline and automatically initiate model retraining to guarantee predictions stay current, can be used to integrate systems.
It is noteworthy that this trend is being accelerated by the emergence of Large Language Models (LLMs), which enable data scientists to automate the creation of synthetic data for testing and the documentation of their code. Even though AI is capable of handling “basic stuff,” data scientists are still valuable in spotting hidden patterns and giving stakeholders the final, useful insights.
Summarising the Future Roadmap
Before delving into more complex AI, one must master foundational skills like SQL, statistics, and mathematics in order to become a data scientist. Professionals who combine traditional statistical knowledge with an understanding of cutting-edge AI tools to increase productivity will be the most successful.
Known as the “Emerging EdTech of India,” WhiteScholars is a Hyderabad-based training and certification facility that offers courses in data science and generative AI.
It offers 100% placement assistance, certifications from Microsoft and Nasscom, and a realistic, hands-on learning environment run by professionals in the field. With real-time projects and a thorough career support system, the academy specializes in helping professionals and novices transition into the tech sector.
WhiteScholars’ six-month program for data science using generative AI is broken down into several phases to help students get ready for the workforce:
- Months 1-2: Foundations of Python and Data Handling Python basics and OOP concepts are covered first, then advanced data handling using web services, web scraping, and Pandas APIs.
- Month 3: Visualization and Statistics Students move on to advanced data analysis and complete data visualization (using Matplotlib and Seaborn) based on a solid grasp of statistics, probability distributions, and inference.
- Month 4: Machine Learning and SQL: This stage focuses on learning advanced SQL for intricate data extraction and manipulation as well as advanced machine learning (both supervised and unsupervised learning).
- Month 5: Deep Learning and Natural Language Processing (NLP): Training progresses to neural network architectures, deep learning foundations, and NLP, including model deployment and productionization.
- Month 6: Reporting Tools and Generative AI In addition to learning Tableau and Power BI for expert reporting, the last phase concentrates on generative AI (including transformers and prompt engineering).
- Career Integration: Students receive assistance with resume construction, LinkedIn optimization, and mock interviews while working on seven or more real-time guided projects and one individual project during the program.
Final Thought
The state of data science in 2026 is a sophisticated combination of automated intelligence and human intuition. The role of the data scientist has evolved from a manual “data cleaner” to a strategic architect of insights as we produce more than 400 million terabytes of data every day. The emergence of AI-driven tools and AutoML has completely changed productivity, even though core libraries like Pandas and NumPy continue to be the cornerstone of the industry.
Even the most sophisticated neural network is useless if it cannot convert a mathematical pattern into an engaging business narrative for stakeholders. In order to close the current “massive skill gap,” aspiring professionals must strike a balance between their technical proficiency with Python and SQL and their strategic ability to find actionable insights. The next industrial revolution will ultimately be led by those who adopt an integrated, AI-enhanced workflow.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. By 2026, what fundamental technical abilities will be required for a career in data science?
You must become proficient in programming languages like Python or R, which provide a wealth of libraries for statistical modeling and numerical computation, in order to be prepared for the workforce. Since machine learning algorithms rely on a strong foundation in mathematics and statistics, this cannot be compromised.
Additionally, managing and presenting data requires mastery of SQL for database querying and visualization programs like Tableau or Power BI. Managing enterprise-scale datasets is made easier with an understanding of big data frameworks like Apache Spark.
2. How can AI tools like GitHub Copilot and AutoML help data scientists?
AI tools automate time-consuming and repetitive tasks like model selection, hyperparameter tuning, and feature engineering. High-accuracy models can be quickly created using platforms like Google AutoML and DataRobot, potentially cutting development time from months to days. GitHub Copilot, on the other hand, serves as an AI assistant that increases coding efficiency by recommending entire functions and code completions. With the help of these tools, data scientists can avoid “basic stuff” and concentrate on resolving more complicated, higher-level problem statements.
3. Why is domain knowledge regarded as a fundamental prerequisite for the position?
The main goal of a data scientist is to solve particular business problems, which necessitates a thorough understanding of the sector they work in, such as finance or healthcare. It is challenging to determine which data is pertinent or to formulate a problem statement that is in line with the organization’s objectives without domain expertise.
Comprehending the business context guarantees that the insights gleaned from unprocessed data are truly useful and applicable to stakeholders. The professional can serve as a liaison between corporate strategy and technical analysis thanks to this expertise.
4. How would one go about becoming a data scientist?
Over the first few months, the journey starts with learning the basics, such as Python, SQL, and basic statistics. In order to show that they can clean data and create models, candidates should then construct real-world projects using datasets from websites like Kaggle.
A thorough exploration of cutting-edge ideas like deep learning and natural language processing (NLP) comes next. The last phases include continuously improving one’s proficiency with new AI tools and learning deployment on cloud platforms like AWS or Azure.
5. Despite the growth of AI, is there still a great need for data scientists?
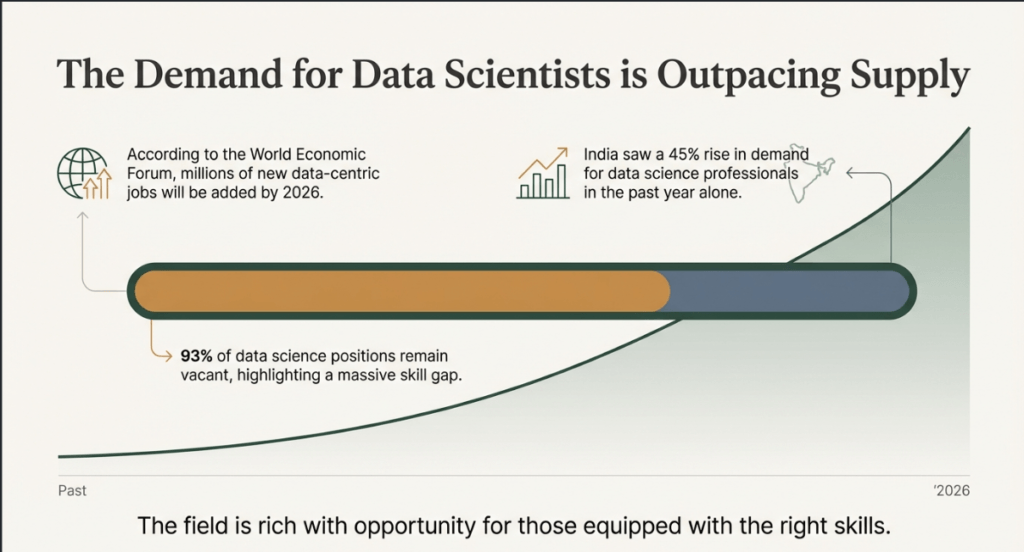
Indeed, demand is soaring; in India alone, the need for data professionals has increased by 45% in the last 12 months. Despite this demand, there is a huge skill gap that prevents employers from finding qualified workers, leaving about 93,000 positions unfilled.
AI can automate some tasks, but it cannot take the place of humans when it comes to working with stakeholders, exercising ethical oversight, or applying complex domain knowledge. Because of this, the industry still pays well to people who can incorporate these new tools into a professional workflow.
