Can a Fresher Learn Data Science Without Any Coding Experience?

Table of Contents
Wondering if you can start a data science career with no coding background? Explore how freshers can learn data science, the tools to start with, and practical tips to build skills from scratch.
What is Data Science?
Data science is fundamentally concerned with the analysis and interpretation of complex data, with the ultimate goal of providing useful insights. The essential core knowledge required of a data scientist lies in statistics and machine learning.
Data science entails mastering a wide range of skills, including programming, mathematical principles, data management, and visualisation techniques.
The Role Of Coding Skills In Data Science
A common misconception in the pursuit of a data science career is the belief that one must start by learning coding languages like Python or SQL. However, coding is merely a tool used to apply data science principles; it is not data science in itself. Data science is rooted in statistics and machine learning, and coding is the vehicle through which a data scientist applies those concepts.
While coding is an important part of the job, aspiring data scientists should first learn the fundamentals of statistics, machine learning, and mathematics. If a candidate discovers that they do not enjoy these, they should stop learning coding languages and instead focus on fundamental concepts. Nonetheless, highly powerful languages such as Python, SQL, and R are required to perform the role.
Landing a data science job requires more than just technical skill acquisition; the process should be treated as a project in itself. Successfully navigating job interviews involves preparation in three key areas: coding, behavioural questions, and, critically, statistics and machine learning fundamentals.
No Prior Coding is Required To Be a Data Scientist
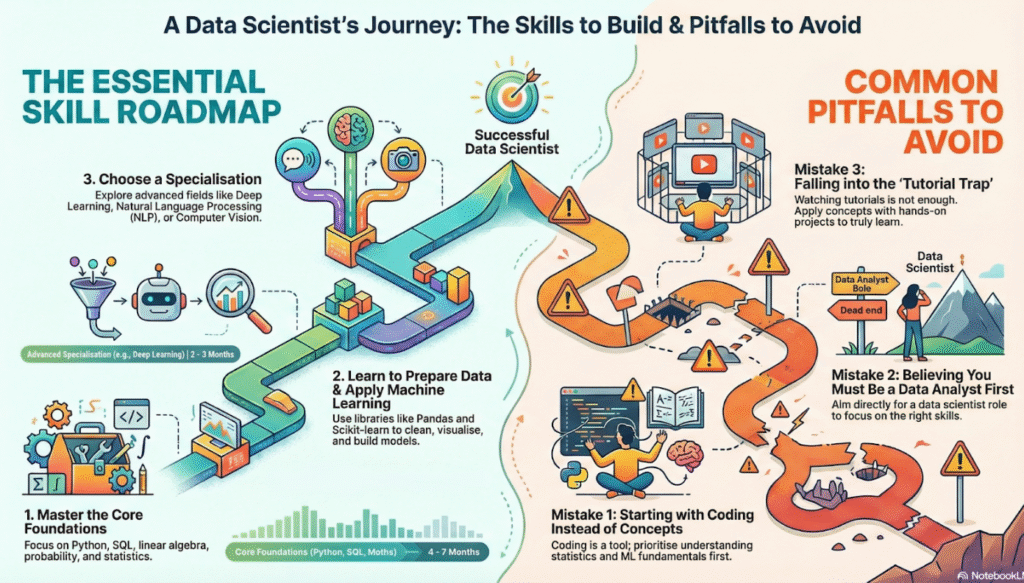
In summary, data science is fundamentally about statistics and machine learning, and individuals should begin their learning journey by mastering these foundational concepts. While languages like Python, R, and SQL are powerful tools and essential for applying data science, starting with coding is considered a mistake if the core knowledge base is not yet established.
Coding is the method of application, not the discipline itself. If the end goal is to become a data scientist, one should start directly with the specific roadmap for that role, rather than pursuing a role like data analyst first, which might divert valuable time away from building expertise in crucial statistics and machine learning concepts and projects.
Consider data science to be the design of a bridge: the fundamental principles of physics, engineering, and material science (statistics and machine learning) must all be fully understood.
Essential Skills Required To Become A Data Scientist
To succeed in the data science domain, candidates must build expertise across foundational principles, technical tools, and professional competencies.
1. Foundational Concepts (Statistics and Mathematics)
A solid foundation in mathematics and statistics is crucial because data science relies heavily on these principles. These topics help data scientists understand data analysis techniques and correctly interpret data.
Key mathematical topics to focus on include:
- Linear algebra.
- Calculus.
- Probability and statistics.
The depth of mathematical knowledge required can vary depending on the specific role a data scientist pursues. If a data scientist wants to create custom machine learning models, they must have a strong mathematical background.
However, if the role primarily involves using already built models, such as standard classification or regression analysis, maths remains important but is required to a lesser degree.
2. Programming, Data Handling, and Visualization Tools
To manipulate and analyse data, data scientists must master a number of key technical tools.
- Python: This is considered the main language in data science due to its versatility and relative ease of learning. Pandas and NumPy are useful libraries for cleaning and manipulating data, whereas Matplotlib and Seaborn are used to create insightful visualisations to identify trends and anomalies.
- R: This is another popular language, known for its strong statistical and visualisation capabilities.
- SQL (Structured Query Language) is a simple language used to interact with databases. Data scientists must understand how to use SQL to access, organise, and analyse the data they require.
- Data Structures and Algorithms: Understanding these concepts is key to boosting problem-solving skills, and these topics are frequently covered in interviews at major tech companies (like Google, Amazon, and Facebook).
- Version Control (Git): Git is a version control system used to track changes to code and collaborate with others, and while it has many features, understanding the most common 20% is usually enough.
- Business Intelligence (BI) Tools: Although not strictly mandatory, getting familiar with tools like Tableau or Power BI is beneficial, as these are widely used in the industry for creating interactive and shareable dashboards.
3. Machine Learning and Deep Learning
After establishing a solid foundation in programming and data handling, expertise in machine learning is required.
- Machine Learning Fundamentals: Algorithms fall into two categories: supervised learning (learning from labelled data with known outputs) and unsupervised learning (figuring out patterns from unlabelled data).
- Machine Learning Tools: Data scientists need familiarity with tools used to build and train models, such as TensorFlow, PyTorch, and scikit-learn.
- Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that employs neural networks with multiple layers. Deep learning is particularly effective at complex tasks such as image and speech recognition. Key knowledge areas include the basics of neural networks and advanced architectures like CNNs and RNNs.
4. Specialized and Big Data Skills
As careers advance, or roles require handling massive datasets, additional skills become important:
- Big Data: This involves handling and processing huge amounts of data quickly. Hadoop and Spark are excellent tools for detecting patterns and trends that may be missed with smaller datasets.
- Data scientists can specialise by becoming experts in fields such as Natural Language Processing (NLP), which deals with text and language data (used for sentiment analysis or creating chatbots), or Computer Vision, which involves teaching computers to interpret visual data (used for object detection or facial recognition).
5. Professional and Business Understanding
Technical skills alone are insufficient for success; data scientists must also have strong soft skills and business knowledge.
- Domain Knowledge and Business Understanding: In order to apply technical concepts in the real world, a data scientist must have strong domain knowledge as well as the ability to understand business requirements.
- Product Management Understanding (PMing): A thorough understanding of the product development life cycle is essential.
- Communication: A successful data scientist must communicate findings, results, and insights effectively to various stakeholders.
Strategic Advice
When starting a career in data science, following a structured plan is paramount. A highly recommended strategy is to work backward: identify a target company and role (e.g., data scientist at Meta), analyse the job description requirements, and research individuals who are currently or have previously worked in that role to create a personal roadmap.
A critical mistake to avoid is the “tutorial trap”, in which concepts appear simple while watching a video or course but are difficult to apply in practice. Success requires hands-on work and moving beyond simply finishing a tutorial. Running into issues during hands-on practice is actually beneficial, as this is often where the most significant learning occurs and knowledge sticks.
Furthermore, aspiring data scientists should leverage modern resources, including generative AI (such as ChatGPT or Bard), which is a transformative technology. Generative AI can help teach new concepts and write basic code, making it an essential component of the learning curriculum.
To successfully carry out the plan, you must first employ the specialised equipment and construction methods (coding and tools). This requires structured training like the White Scholars Data Science course in Hyderabad.
The program is designed to bridge the gap between academic learning and real-world skills, offering a clear path from basics to advanced concepts like machine learning, generative AI, SQL, and Tableau. Its structured approach ensures students progress step by step, with guidance from expert mentors and guest lectures by industry leaders. Flexibility is a big advantage here.
The hybrid mode of learning allows you to attend offline classes, join online sessions, or access recorded lectures anytime, making it easy to balance studies with other commitments.
Students also benefit from strong placement support, guaranteed interview opportunities, and internships with top companies. With 7+ real-time projects, capstone assignments, and Nasscom and Microsoft certifications, students graduate with both hands-on experience and recognised qualifications.
This combination of structured training, hands-on projects, and career support makes White Scholars’ data science course in Hyderabad a standout choice for aspiring data scientists.
Final Thoughts
Data science is fundamentally rooted in statistics and machine learning, with coding serving strictly as a tool for application. While powerful programming languages such as Python, SQL, and R must be learnt, the critical mistake is to begin coding before mastering the fundamental concepts of statistics, machine learning, and mathematics.
Coding is one of three critical areas of job interview preparation (the other two being behavioural questions and fundamentals). The job market has been “stressful” in recent years, but positions such as AI product manager have become “hot topics.”
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Do I need coding skills to begin data science?
A. Not at all. Many people assume data science is only for programmers, but the truth is you can start without writing a single line of code. Beginner-friendly tools like Excel, Power BI, and Tableau allow you to explore data visually, create dashboards, and understand insights. This means you can focus on learning how data tells a story before diving into technical coding.
2. What skills should I focus on first?
A. Rather than worrying about programming, begin with the fundamentals: statistics, logical thinking, and data visualisation. These skills help you understand patterns, trends, and how to interpret results. Once you’re comfortable, you can gradually add coding languages like Python or R to your toolkit.
3. Can I still work on projects without coding?
A. Yes, absolutely. Drag-and-drop tools can be used to analyse sales data, customer feedback, and social media trends. You’ll be surprised how much you can achieve with charts, graphs, and dashboards. These projects give you practical experience and confidence before you move into coding-heavy tasks.
4. How do courses help beginners with no coding background?
A. Structured courses are designed to guide you step by step. For example, the White Scholars’ Data Science programme in Hyderabad begins with fundamentals such as statistics and visualisation before gradually introducing coding with hands-on support. This way, non-coders don’t feel overwhelmed.
5. Will I need coding eventually?
A. Yes, coding becomes important as you advance. It helps automate tasks, handle large datasets, and build machine learning models. But don’t let that scare you; by the time you reach that stage, you’ll already have a strong foundation in data analysis. With the right guidance, coding will feel like a natural extension of what you’ve already learnt.
