Data Scientist 2026: Essential things to Know
Table of Contents
Planning to become a data scientist in 2026? Then you are at the right place. Here are the key insights that every aspiring learner must know about data science.
Why 2026 is a Game-Changer for Data Science
The year 2026 marks a significant shift in data science. While the field previously focused on analysing historical data to understand past events, it has evolved into a discipline centred on predicting the future and enabling real-time decision-making.
- Growth and Demand: The demand for data scientists is projected to increase by 35% in the coming years, a rate much faster than the average for other occupations. Data scientists remain among the highest-paid professionals globally.
- Technological Shifts: The roadmap has been refreshed to account for the dominance of AI automation, generative AI, and real-time analytics. Businesses no longer just want to see data; they want data to “work for them” by creating new products, ideas, and content.
- Personalisation: Data science is now at the heart of tailored consumer experiences, such as the curated shopping suggestions seen on major online platforms.
- AI Ethics: As AI becomes more integrated into business, AI ethics has emerged as a critical focus area. Companies are actively seeking experts who can ensure AI is used responsibly and ethically.
The Core Foundations of Data Science
To succeed in 2026, you must master several foundational technical and cognitive skills. These form the base upon which all advanced machine learning and AI applications are built.
Python Mastery (with Pandas and NumPy)
Python is considered a data scientist’s “best friend” due to its simplicity and its power to handle complex datasets. However, general Python knowledge is insufficient; proficiency in specific libraries is required:
- Pandas: Acts as a “toolbox” for managing and analysing data. It allows you to read, clean, and organise data, much like an advanced, programmatic version of a spreadsheet. For example, a data scientist might use Pandas to sort and filter thousands of customer orders in just a few lines of code.
- NumPy: Functions as a high-speed “calculator” for numerical data. It is essential for performing complex mathematical operations, such as calculating average sales or modelling how external factors like weather impact a business.
SQL (Structured Query Language)
SQL is indispensable for querying and analysing data stored in massive databases. It is the primary language used to communicate with databases to extract specific information.
- Practical Use: If a company needs to identify which product sold the most in the previous month, a data scientist uses SQL to query the sales database, group the data by product, and filter for the specific timeframe. SQL is vital for filtering through “noise” to find precise insights.
Statistics for Data-Driven Decisions
Statistics is the science of collecting and interpreting data to make decisions based on numbers rather than guesses. It allows data scientists to identify patterns and trends in behaviour.
- Descriptive Statistics: Tools like averages, percentages, and distributions help summarise what is happening. For instance, a bakery owner might use statistics to find the average number of cupcakes sold per hour to decide when to bake more or adjust marketing efforts.
- Inferential Thinking: Statistics helps answer questions regarding the probability of a customer buying a product or the likelihood of a specific trend continuing.
Problem Solving and Analytical Thinking
Data science is not just about coding; it is about critical thinking.
- Structured Approach: When faced with a business challenge (e.g., predicting which customers will buy a new product), a data scientist must break the problem down into manageable steps: identifying necessary data, cleaning it, finding patterns, building a model, and presenting actionable findings.
- Multiple Angles: Analytical thinking involves looking at a problem from various perspectives and testing ideas with data to see if a solution actually works.
Advanced Skills for 2026
To stand out in a competitive market, data scientists must move beyond the basics into advanced modelling and emerging AI technologies.
Machine Learning (Scikit-learn and TensorFlow)
Machine learning involves creating systems that learn from data to make predictions without being explicitly programmed.
- Scikit-learn: Described as a “beginner toolkit”, this library is used for building models quickly, such as classifying images, predicting stock prices, or detecting spam emails.
- TensorFlow: A more advanced library used for complex tasks, particularly in deep learning. It is used for high-level applications like image recognition, language translation, and autonomous driving.
Deep Learning
Deep learning is a subset of machine learning that uses neural networks inspired by the human brain.
- When to Use: Deep learning is the preferred choice for unstructured data like images, video, and sound. For example, while standard machine learning might be used to predict house prices (structured data), deep learning would be used to distinguish between photos of cats and dogs.
Generative AI and Prompt Engineering
This is currently one of the most rapidly growing areas in AI.
- Generative AI: Unlike traditional AI that analyses data, GenAI creates new data, such as text, images, or music. Tools like ChatGPT and Google Gemini are primary examples.
- Prompt Engineering: This is the skill of interacting effectively with GenAI tools. It involves crafting precise instructions to get the most accurate results, such as asking an AI to “write a 500-word blog post explaining the basics of data science with examples”.
Natural Language Processing (NLP)
NLP is the branch of AI that allows computers to understand, interpret, and generate human language.
- Applications: It powers voice assistants like Siri and Alexa, as well as website chatbots. In a business context, NLP can be used to analyse thousands of product reviews to determine what customers like or dislike about a product, turning “messy” text into insights.
Time Series Forecasting and Anomaly Detection
These techniques are essential for data that changes over time, such as stock prices or weather patterns.
- Forecasting: Uses past data to predict future trends, helping businesses plan for the upcoming month or year.
- Anomaly Detection: Identifies unusual patterns, such as a sudden spike in website traffic, which could indicate a successful marketing campaign or a security threat.
Essential Tools and Platforms
Mastering the right software ecosystem is crucial for efficiency and collaboration.
- Development Environments: Jupyter Notebook is used for testing, visualising, and explaining code in a digital notebook format. VS Code is a powerful editor for writing and debugging code.
- Collaboration: Git and GitHub are mandatory for tracking changes in code and working within teams on large projects.
- Cloud Platforms: AWS, GCP, and Azure provide the infrastructure to store and process massive datasets using “supercomputing in the sky” without needing specialised local hardware.
- Big Data Tools: Spark is a fast engine for processing large datasets. Databricks (built on Spark) helps deploy machine learning models at scale, and Snowflake provides a cloud-based platform for analysing data from various sources.
- Visualisation: Tableau and Power BI is used to create interactive charts and dashboards for business stakeholders. Plotly is a Python-based tool for deeper, interactive data insights.
Want to excel at learning all trending tools? Then enrol yourself for White Scholars: Data science Course with generative AI
Building a Job-Winning Portfolio
A portfolio must demonstrate that you can solve real-world problems.
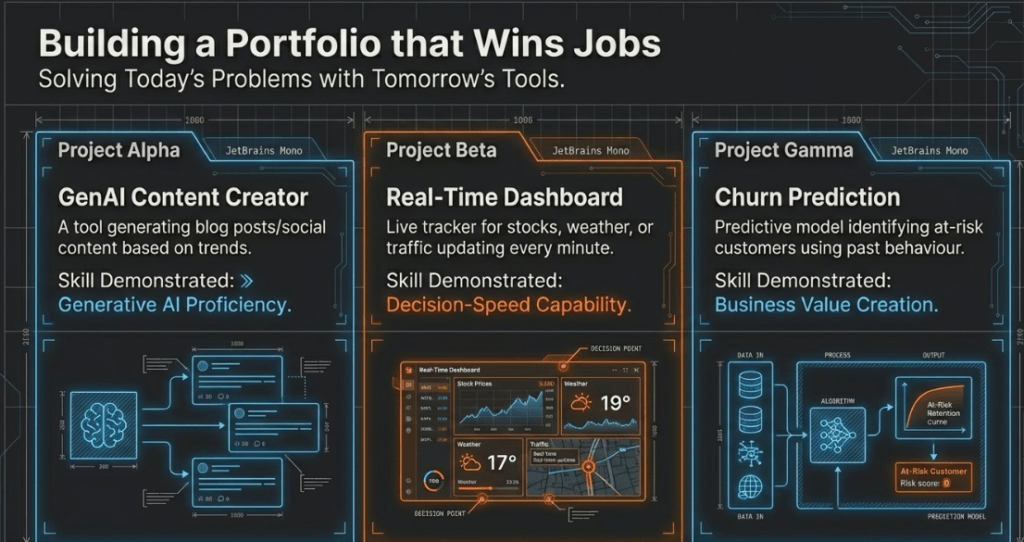
Project Ideas
- GenAI for Content Creation: Build a tool that generates social media posts based on trending topics.
- Real-Time Dashboards: Create a live-updating dashboard for stock prices or weather data.
- Customer Loss Prediction: Use past purchase behaviour and feedback to predict which customers are likely to leave a service. This is a highly valued predictive modelling project across many industries.
Visibility and Collaboration
- Kaggle: Participate in competitions to solve global data problems, such as house price prediction or image classification.
- Open Source: Contribute to projects on GitHub by fixing bugs or adding features to machine learning algorithms.
- Personal Branding: Maintain a GitHub directory and a personal blog. Use these to share tutorials and “walkthroughs” of your projects, which demonstrates your communication skills to recruiters.
The Power of Storytelling
A portfolio should not just show code; it should tell a story. Use the Problem-Solution- Results framework:
- Problem: Define the challenge (e.g., “I needed to predict customer loss for a subscription service”).
- Solution: Describe the technical approach (e.g., “I cleaned data, used feature engineering, and trained a random forest model”).
- Results: State the outcome (e.g., “The model achieved 85% accuracy and helped retain 15% more customers”).
Choosing Your Career Path
Data science is a broad field with several specialised roles. Choosing the right one depends on your interests.
- Data Analyst: The “detectives” who find trends, visualise insights, and generate reports using Excel, SQL, and Tableau.
- Data Engineer: The “builders” who design the infrastructure and pipelines that allow companies to manage massive amounts of data.
- Data Scientist: The “problem solvers” who use advanced statistics and machine learning to find patterns and make predictions.
- Machine Learning (ML) Engineer: Focus on the technical side of taking models and turning them into large-scale production systems.
- AI Product Manager: A hybrid role for those interested in both AI and business strategy, leading teams to develop AI-driven products.
- Data Ops Engineer: Similar to DevOps but for data; they focus on automating and streamlining data flows across an organisation.
Landing the Job: Resume, Interviews, and Salary
Resume Best Practices
- Do: Highlight modern skills (Python, SQL, GenAI), show your impact with specific results (e.g., “increased sales by 15%”), and keep the design simple and concise.
- Don’t: overload the resume with technical jargon, list outdated skills (like only listing Excel), or forget to include personal projects and Kaggle achievements.
Interview Preparation
- Be ready to explain complex algorithms to non-technical people.
- Practice walking through your projects, explaining the problem, your specific solution, and the final results.
- Understand technical concepts (machine learning models, statistical tests) deeply rather than just memorising facts.
Salary Expectations
- United States: Salaries typically range from $70,000 to $130,000.
- India: Starting salaries range from 6 lakh to 15 lakh INR, with the potential for much more at top-tier companies.
Work Models: Remote vs. On-Site
- Remote Work: Offers flexibility and better work-life balance but may lack networking opportunities and face-to-face communication for complex ideas.
- On-Site Work: Provides better networking, structured environments, and quicker feedback but involves commutes and less flexibility.
Continuous Learning and Training
Data science is evolving so rapidly that continuous learning is mandatory. Staying updated via blogs, LinkedIn, and community platforms like Kaggle and GitHub is recommended.
- White Scholars Data Science Course with Generative AI: a 6-month live program in collaboration with Microsoft. It covers Python, SQL, and machine learning through interactive sessions with industry experts and includes a capstone project and professional certification.
By following this roadmap, mastering foundations, advancing into AI and GenAI, using the right tools, and effectively showcasing your work, you will be well-positioned to lead in the data science landscape of 2026.
Final Thoughts
The year 2026 represents a pivotal shift where data science moves from analysing the past to predicting the future through AI automation and real-time analytics.
Mastering foundational skills like Python and SQL while embracing advanced concepts like generative AI and NLP is essential for staying competitive.
Building a strong portfolio using Kaggle and GitHub allows you to showcase problem-solving abilities and storytelling. With demand projected to grow by 35%, starting your journey now offers a significant edge in landing high-paying roles in this rapidly evolving landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Why is 2026 considered a game-changer for data science?
Data science is shifting from historical analysis to making data work for you through generative AI, real-time analytics, and AI automation. The focus is now on predicting the future and creating highly personalised consumer experiences.
2. What are the must-have foundational technical skills?
You must master Python, specifically the Pandas library for data organisation and NumPy for numerical calculations. Additionally, SQL is essential for querying databases, and statistics is required to identify patterns and trends.
3. What is the difference between machine learning and deep learning?
Machine learning uses tools like Scikit-learn to make predictions from structured data, while deep learning uses neural networks to process complex, unstructured data like images, video, and sound.
4. How can I make my data science resume stand out to recruiters?
Highlight modern skills (GenAI, Python, SQL) and show your impact with specific results, such as building a system that increased sales by a certain percentage. Avoid outdated skills, and ensure your GitHub projects or Kaggle wins are clearly listed.
5. What are the salary expectations for data scientists in this roadmap?
In the United States, salaries generally range from $70,000 to $130,000. In India, roles typically start between 6 lakh and 15 lakh INR, with significantly higher potential at top-tier companies.
