Generative AI Masterclass: Roadmap and Deep Dive into GANs
Table of Contents
A clear guide to generative AI with a beginner roadmap and a technical deep dive into GAN architectures powering modern AI.
Introduction
The world of technology has undergone a seismic shift, moving from traditional computing to an era dominated by AI. Since 2023, generative AI (GenAI) has emerged as a disruptive force, rapidly progressing from science fiction to a functional novelty and, finally, to the very foundation of the future.
1. The Economic and Professional Landscape of Generative AI
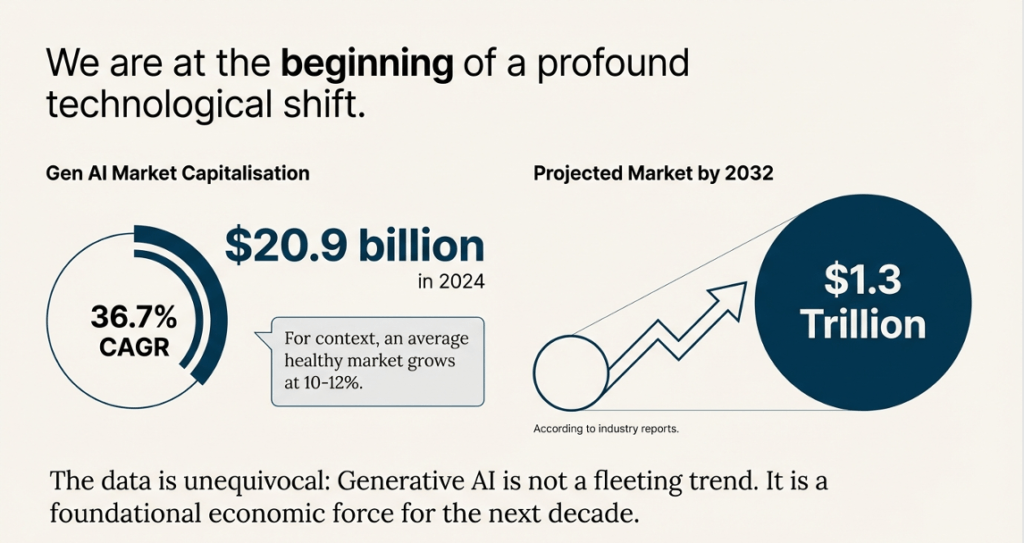
The rise of generative AI is more than a trend; it is backed by staggering financial data. The market capitalisation of Gen AI is expected to reach $20.9 billion by 2026, representing a 36.7% compound annual growth rate (CAGR). To put this in context, typical market growth in India has a growth rate of 10% to 12%, making Gen AI particularly rapid. According to reports, this sector will reach $1.3 trillion in value by 2032.
The impact of this expansion is most visible in the “white-collar” sector. While early discussions focused on manufacturing automation, AI is now capable of performing complex tasks that were once reserved for office professionals. This shift has raised significant ethical and privacy concerns about the misuse of AI, despite the fact that tech behemoths like Microsoft invest billions of dollars in organisations like OpenAI.
2. The Two Paths to Mastery: User vs. Engineer
For absolute beginners, there are two types of engagement with generative AI:
- The user/prompt engineering path entails learning how to use existing AI tools efficiently. It emphasises prompt engineering, which is the practice of creating queries that produce the best results from Large Language Models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT. For example, a vague prompt like “write an essay on deforestation” yields a broad result, whereas a detailed prompt specifying Indian news, industrial impacts, and specific structural requirements yields a far more refined result.
- The Engineering/Implementation Path: This is a more difficult path that requires understanding how AI tools are created and work behind the scenes.
3. The 2026 Engineering Roadmap for Beginners
If you choose the engineering path, you will go through several structured steps to advance from beginner to proficient AI engineer.
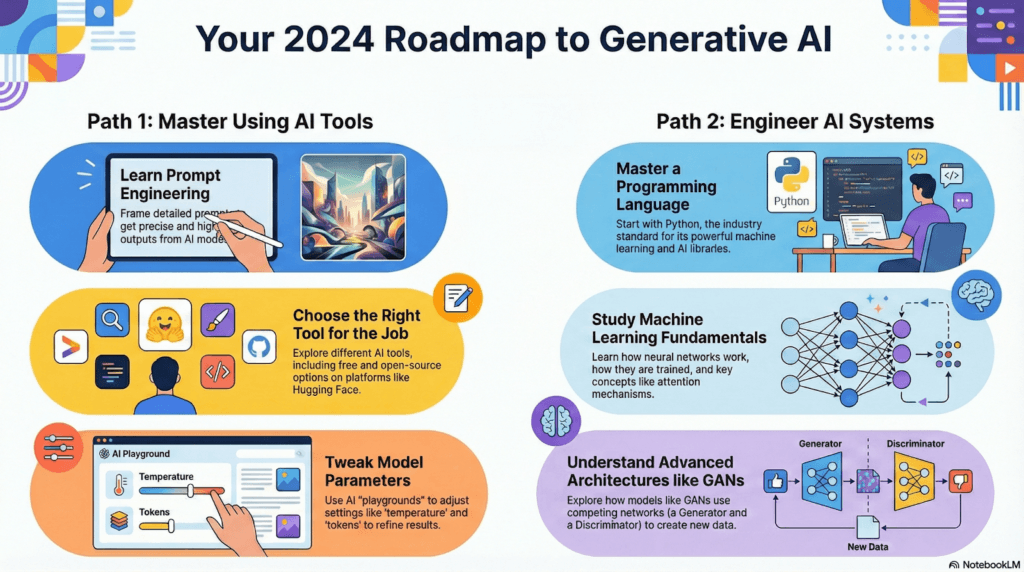
Step 1: Programming Foundation
The primary language recommended for GenAI is Python, but JavaScript is also mentioned for its usefulness in developing web applications that use AI APIs. Python is popular due to its extensive libraries and dominant position in the machine learning ecosystem.
Step 2: Using APIs and Existing Tools
Before starting from scratch, engineers can use APIs provided by companies such as OpenAI to create “AI-powered” apps. This allows you to create functional software without having to first understand the model’s deep mathematics.
Hugging Face, for example, contains a large number of models that can be used for tasks such as subtitle generation and audio transcription. For example, OpenAI’s Whisper model can be run locally or hosted on services such as AWS to generate automated subtitles.
Step 3: Machine Learning and Deep Learning Theory.
To proceed with true implementation, you must understand:
- Neural networks are the fundamental architecture of AI.
- Gradient descent is an optimisation algorithm used to train models.
- Hyperparameters include concepts like temperature (which governs the randomness of AI responses) and tokens (the model’s text processing components).
Step 4: Advanced architectures
The publication of the paper “Attention Is All You Need,” which first introduced the attention mechanism, was a watershed moment in GenAI history. This mechanism enables models to focus on specific parts of an input sequence, transforming the way text and data are processed.
4. Understanding Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
While LLMs dominate text generation, Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) are the powerhouses behind image, video, and music generation. GANs, developed by Ian Goodfellow, in 2014, enabled machines to generate new, realistic data by learning from existing examples.
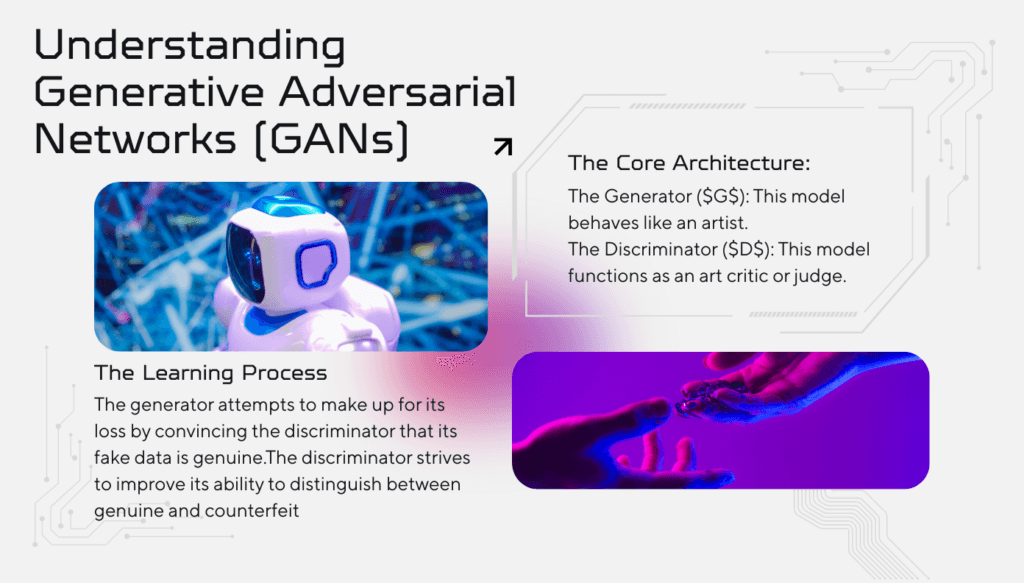
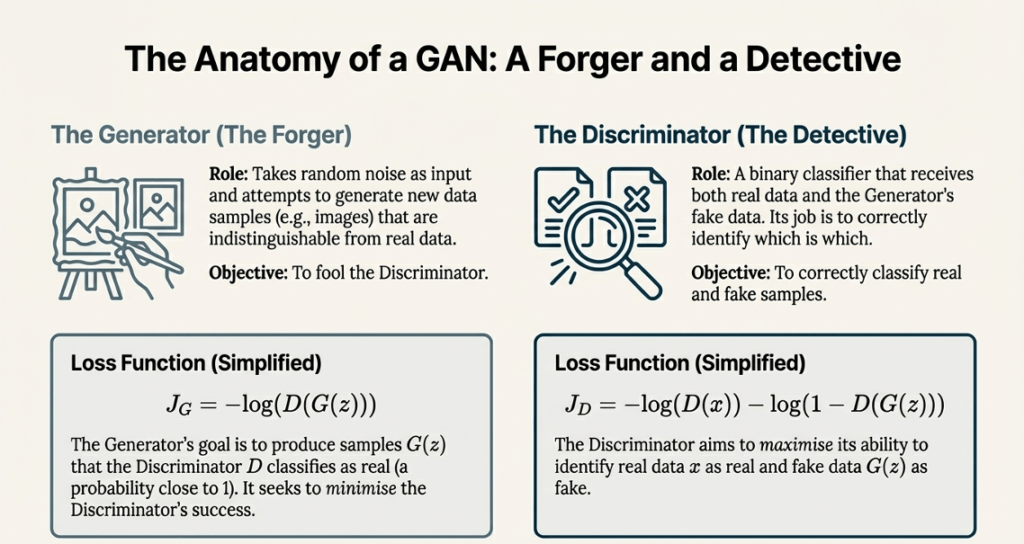
The Core Architecture
A GAN is composed of two neural networks that compete in a “zero-sum game”:
- The Generator ($G$): This model behaves like an artist. It accepts random noise as input and attempts to convert it into a realistic data sample (such as an image). The goal is to create “fakes” that are convincing enough to fool the second model.
- The Discriminator ($D$): This model functions as an art critic or judge. It is a binary classifier that accepts both real data (from a training set) and simulated data (from the generator). Its job is to correctly identify which is which, generating a probability score of 1 for real and 0 for fake.
The Learning Process: Adversarial Training
A GAN’s training involves constant back-and-forth.
- The generator attempts to make up for its loss by convincing the discriminator that its fake data is genuine.
- The discriminator strives to improve its ability to distinguish between genuine and counterfeit. This competition, known as MinMax Loss, eventually leads to a situation in which the generator is so skilled that the discriminator can no longer tell the difference between synthetic and real data.
5. Types and Variations of GANs
GANs have evolved into several specialised forms to handle a variety of tasks:
- Vanilla GAN: The most basic form of multi-layer perceptrons. It frequently experiences mode collapse, which occurs when the generator consistently produces the same limited output.
- Conditional GAN (CGAN): This version supports targeted generation. By providing a label (such as “dog” or “cat”), you can instruct the GAN to generate a specific type of image rather than a random one.
- Deep Convolutional GAN (DCGAN): These are the most widely used for image generation. They replace simple layers with Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs), which are much better at comprehending spatial features in images.
- Super Resolution GANs (SRGANs) are used to improve low-quality images by adding finer details, making them sharper and more realistic.
- Laplacian Pyramid GAN (LAPGAN): These generate ultra-high-quality, photorealistic images by combining multiple generator-discriminator pairs at various resolutions.
6. Implementing a GAN in PyTorch
For those interested in engineering, a detailed implementation of the PyTorch library on the CIFAR-10 dataset.
- Transformations: To ensure training stability, images are converted to tensors and normalised in the range of -1 to 1.
- Hyperparameters: Key settings include the latent dimension (the size of the random noise vector, which is typically set to 100), the learning rate (e.g., 0.0002), and Adam optimisers with specific beta values.
- Building the generator: It uses nn.Upsample to improve resolution and nn.Conv2d to refine features, followed by a Tanh activation to scale the output.
- To prevent overfitting, the discriminator is composed of convolutional layers with LeakyReLU and dropout, followed by a probability-generating sigmoid layer.
- Training Loop: The discriminator is trained on real and fake batches first, and the generator is updated based on how well it “fooled” the discriminator with binary cross-entropy (BCE) losses.
7. Real-World Applications and Advantages
Generative AI, specifically GANs, has numerous applications:
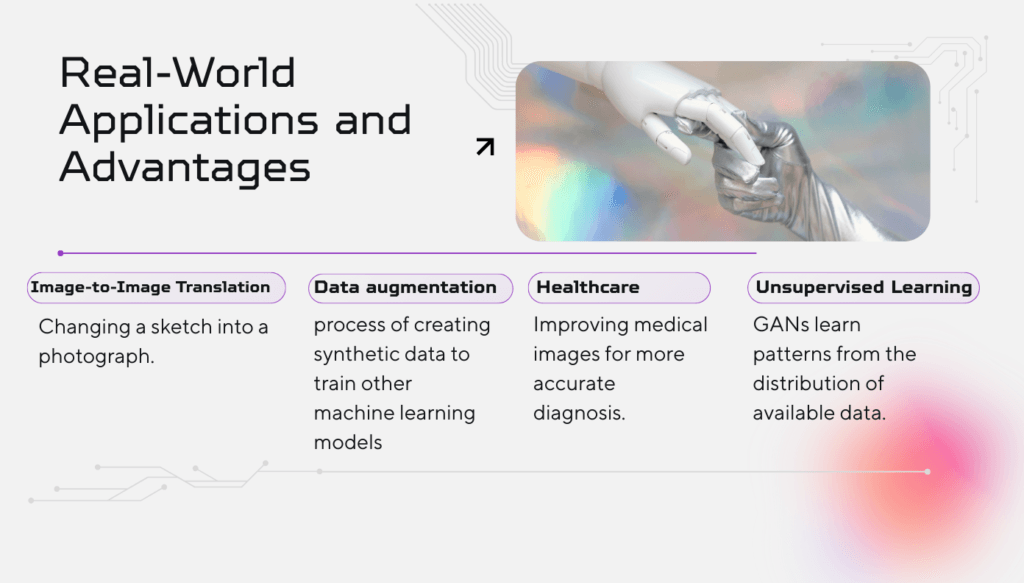
- Image-to-Image Translation: Changing a daytime scene to a nighttime scene, or a sketch into a photograph.
- Data augmentation is the process of creating synthetic data to train other machine learning models when real data is scarce.
- Healthcare: Improving medical images for better diagnosis.
- Unsupervised Learning: GANs are effective because they do not always require expensive, human-labelled data; instead, they learn patterns directly from the distribution of available data.
8. Personal Insights and Interesting Points (External Information)
- The Concept of Hallucination: While the world emphasises Gen AI’s creativity, one major industry challenge is hallucination, in which models generate factually incorrect but convincing information. This is why human-in-the-loop verification is still important.
- Agentic AI is the next frontier in which AI not only generates content but also performs autonomous actions such as flight booking or project management through agents.
- Compute Costs: The cost of GPUs is a significant barrier to entry for developing high-level GANs and LLMs. Amazon Web Services: Many developers are now using “Low-Rank Adaptation” (LoRA) to fine-tune large models on consumer-grade hardware.
Generative AI Masterclass: Why WhiteScholars is the Right Choice
Joining the White Scholars Data Science Course with Generative AI specialisation is a strategic step towards success for students interested in a career in data science and artificial intelligence.
The course is designed to provide practical learning rather than theoretical knowledge. Experienced trainers guide students through each stage of the learning process, from learning the fundamentals of Python and NumPy to mastering advanced topics such as GANs, deep learning, and generative models.
Another significant advantage is the hybrid learning model. Students can take classes both online and offline, making it convenient for those who work or are pursuing other studies. White Scholars ensures that students gain not only technical expertise but also the confidence to present themselves professionally in front of recruiters through mock interviews and communication sessions.
White Scholars is particularly appealing to students who value clarity and structure in their education. The teaching style is straightforward, visual, and example-based, making even complex topics such as GANs simple to grasp. The emphasis on infographics, slides, and visual aids allows students to grasp concepts quickly and retain them longer. Furthermore, the institute encourages students to improve their work for accuracy and presentation, fostering habits that are necessary in professional settings.
Students receive a comprehensive package that prepares them for the rapidly evolving world of generative AI, including strong mentorship, practical projects, flexible learning, and placement support.
Final Thought
Generative AI represents a fundamental shift in how we interact with technology, rapidly expanding from a novelty to a $1.3 trillion market potential by 2032. For those on the verge of this revolution, the choice is clear: remain a user of existing tools through proactive engineering or become an engineer who builds tomorrow. While the engineering path is significantly more difficult, requiring a thorough understanding of neural networks, gradient descent, and complex architectures such as GANs, the rewards are significant due to high demand and a scarcity of experts.
Mastering Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) represents the pinnacle of creative engineering. Machines can now generate realistic synthetic data that is similar to the real world by training two competing models: the Generator and the Discriminator. Adversarial training has enabled previously unattainable capabilities in image synthesis, medical imaging, and data augmentation.
However, technical knowledge alone is insufficient; practitioners must keep up with foundational research like the “Attention Is All You Need” paper, as well as practical implementations using frameworks like PyTorch.
Personal Insight: The next stage of this evolution will most likely be agentic AI, in which models solve multi-step problems autonomously rather than simply creating content. This shift emphasises the importance of the engineering path, as the world will need architects to build these self-sufficient systems.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
What is generative AI, and why does it matter?
A. Generative AI refers to algorithms capable of producing new data such as images, text, or audio. It is important because it enables innovations such as realistic image generation, chatbots, and personalised recommendations. GANs are an important part of this because they train two networks to compete and improve results.
What is a GAN, and how does it work?
A. GANs, or Generative Adversarial Networks, are made up of two models: a generator and a discriminator. The generator generates fake data, and the discriminator determines whether it is real or not. The generator improves with repeated training, eventually producing highly realistic outputs.
What skills are required to learn generative AI?
A. Students should have a solid understanding of Python, statistics, and machine learning. Knowledge of deep learning frameworks such as TensorFlow and PyTorch is also useful. White Scholars guides beginners step by step, making it accessible to students from business or non-technical backgrounds.
What are the practical applications of generative AI?
A. Generative AI is used in healthcare, marketing to create personalised ads, finance to detect fraud, and entertainment to create art or music. Its applications are rapidly expanding, making it an essential skill for future careers.
Why should I choose White Scholars Hyderabad to pursue generative AI?
A. White Scholars provides structured mentorship, hybrid learning, and placement services. Unlike many other institutes, it provides both technical and communication training. Students work on real-world projects, practise their presentation skills, and receive guidance until they are ready for interviews. This makes it one of the best places to learn generative AI in Hyderabad.
