Guide to Generative Engine Optimization: Strategies and more
Table of Contents
GEO assists in structuring and refining content that needs to be summarized. Let’s focus on the guide to generative engine optimisation.
What is Generative Engine Optimization (GEO)?
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO), also called LLMO or AI search optimization, is the method of organizing and improving digital content so that artificial intelligence can easily analyze, summarize, and reference it.
While traditional search engine optimization (SEO) focuses on increasing clicks from a list of links on a search results page, GEO seeks to improve the readability and meaning of content for large language models (LLMs) such as ChatGPT, Gemini, Perplexity, and Google’s AI Overviews.
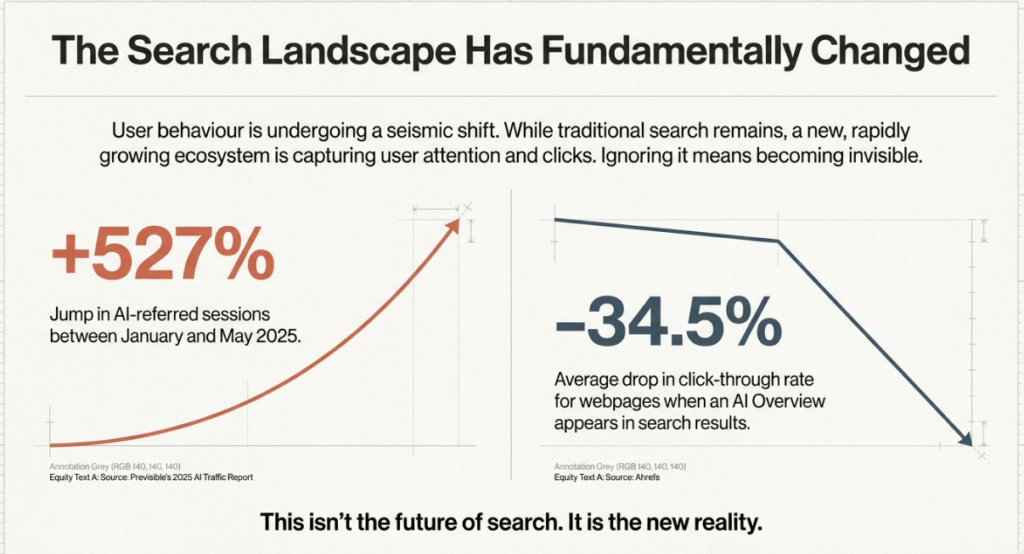
The main aim is to include your brand’s details in AI-generated answers, which users are starting to like more than regular browsing. This approach is becoming more crucial, as sessions referred by AI rose by 527% in the first half of 2025, showing a big change in how people access information.
For instance, think about a company using software to handle repetitive marketing tasks like sending emails, posting on social media, and nurturing leads. This technology helps marketing teams create personalized experiences for their audience while saving time for more important strategic activities.
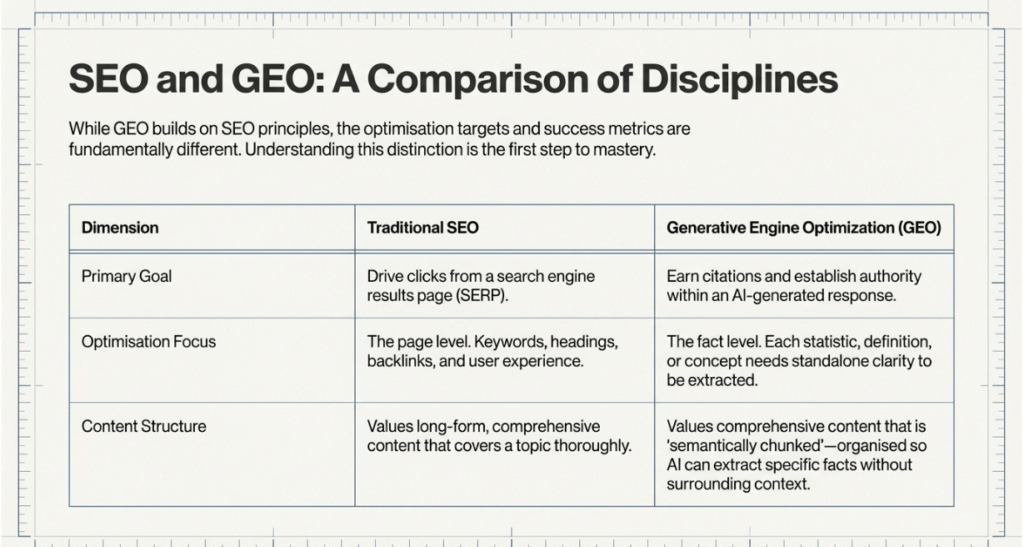
In the case of traditional SEO, it aims to rank high for clicks using keywords and backlinks. In contrast, GEO focuses on making content easy for AI to reference. It begins with a clear definition in the first 40-60 words to facilitate extraction. GEO also adds relevant statistics for every 150 to 200 words and organizes information into clear sections. While SEO targets website visits, GEO positions your brand as a trusted source in AI-generated summaries.
The Fundamental Shift: SEO vs. GEO
GEO builds on SEO but has different goals and success measures. SEO aims to get clicks from people, measured by rankings and click-through rates (CTR). In contrast, GEO is meant for AI models to reference, focusing on building authority and brand presence in discussions.
A critical reason for this shift is the rise of “zero-click” searches. Industry research indicates that roughly 65% of Google searches now end without a click to a website because AI Overviews and snippets answer the user’s query directly.
Furthermore, when an AI Overview appears, the average CTR for the top organic results drops by 34.5%. In this environment, “owning the answer” becomes more valuable than merely ranking for a keyword.
Mechanics of AI Search: Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG)
To optimize for generative engines, one must first understand the underlying technology, Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG). This process occurs in several distinct steps:
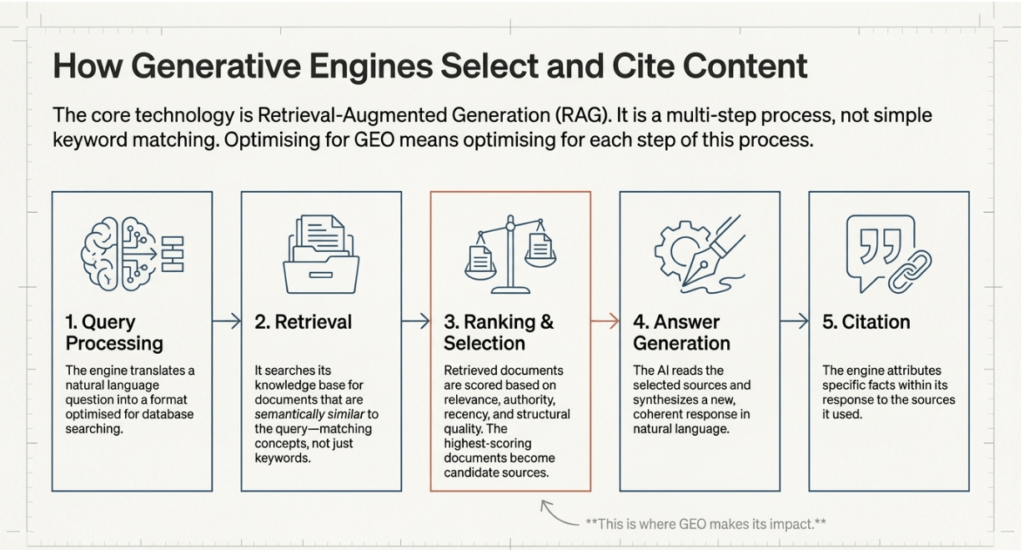
- Query Processing: The engine converts a user’s natural language prompt into a semantic representation (concept matching rather than just keyword matching).
- Retrieval: The system searches its internal training data or external web indices for documents that are semantically similar to the query.
- Ranking and Selection: Retrieved documents are scored based on authority, recency, relevance, and structural quality. This is the stage where GEO-optimized content gains an advantage.
- Answer Generation: The AI synthesizes the information from the selected sources into a coherent, natural-language response.
- Citation Inclusion: The engine attributes specific facts to the sources used, often via inline citations or footnotes.
How Generative Engines Process Information
Generative engines do not simply copy and paste text; they generate unique responses each time based on patterns in data. Some engines, like Perplexity, run multiple background web searches and cite sources directly, while others, like ChatGPT’s O3 model, are trained to think and process queries more deeply before generating an output.
A key feature of these engines is that they rewrite complex queries. They break down long sentences or paragraphs into smaller chunks that the model can process, allowing for more conversational and multi-faceted searches than traditional search engines.
Because different engines use different data sets and crawling methods, some relying on web results and others on pre-trained data, GEO tactics must be broad enough to reach across various platforms.
The Three Pillars of GEO Success
Research conducted by Princeton University, Georgia Tech, and Stanford has identified three specific content characteristics that can boost AI visibility and citation frequency by 40%.
1. Citing Authoritative Sources
Content that shows strong research by linking to .edu, .gov, or peer-reviewed studies gets more citations. AI engines like content based on facts instead of guesses. Adding citations for important claims or statistics tells the AI that the content is trustworthy and reliable.
2. Adding Direct Quotations
Using direct quotes from experts adds credibility. AI models recognize quotes as facts or expert opinions. Well-formatted quotes with clear attribution, like the expert’s credentials, create the citable pieces that AI engines prefer.
3. Including Statistics
Content with lots of facts is more often cited because users frequently ask AI engines for numbers (like, “What is the ROI of X?”). It’s best to keep a high number of facts, aiming to include a statistic, percentage, or number every 150-200 words.
Platform-Specific Optimisation
Different platforms have unique preferences for how they select content for citations.
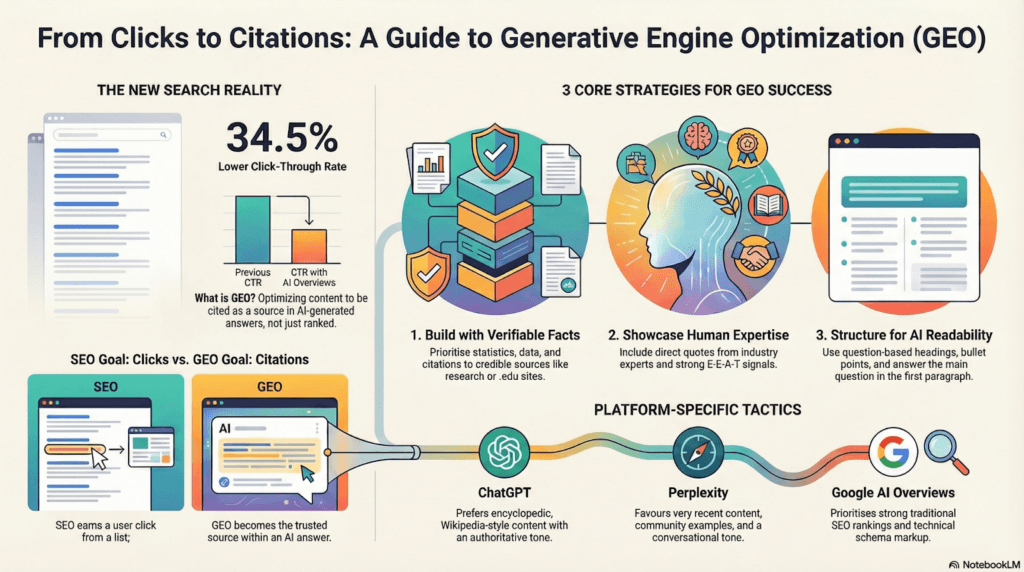
- ChatGPT: Favors an encyclopedic, neutral, and third-person tone similar to Wikipedia. It prefers comprehensive resources (averaging 2,800 words) and content structured with clear definitional sections and comparative listicles.
- Perplexity: Focuses on recent and community-approved content. It often references sites like Reddit and prefers real-life examples or case studies (e.g., “how we did X”) instead of just theory. Freshness is important, favoring content published in the last 90 days.
- Google AI Overviews: Relies heavily on existing organic rankings and E-E-A-T signals (Expertise, Experience, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness). Content that already ranks in the top 10 and uses structured data markup is most likely to be featured.
Content Structure for LLM Interpretability
For AI to process and cite your content, it must be structured logically.
- Answer-First Structure: Include the direct answer to the primary question within the first 40-60 words. This allows AI engines to extract the core concept easily for a citation.
- Semantic Chunking: Every section (marked by H2 or H3 headings) should be independent. An AI engine should be able to extract a single paragraph or section and have it make sense without the context of the rest of the article.
- Question-Format Headings: Converting headings into questions (e.g., “How does X work?”) maps directly to how users query AI platforms, increasing the likelihood of relevance.
- Conversational Tone: Writing in a style that mirrors natural speech helps AI models better understand the context and intent of the information.
Identifying GEO Opportunities and High-Value Queries
To begin a GEO workflow, businesses should identify where they already have a foothold.
- Filter for Top 10 Rankings: Use tools to find keywords where your site already ranks in positions 1-10. This is your foundation for winning AI citations.
- Isolate AI Overviews: Identify which of these keywords trigger an AI Overview.
- Segment Owned vs. Unowned: Distinguish between “Owned AIOs” (where you are cited) and “Unowned AIOs” (where an overview exists but you are missing).
- Prioritize Commercial Intent: Concentrate your optimization efforts on high-value, revenue-generating queries or branded product searches with a high conversion rate.
The Role of E-E-A-T and Brand Positioning
AI models prefer reliable and influential content. Enhancing E-E-A-T is a key quality indicator. This means using knowledgeable writers, sharing personal experiences, and keeping the brand description consistent online.
Brand positioning matters too. Brands that use clear phrases (like “science-backed skincare”) in press releases, product descriptions, and discussions on Reddit or Quora are more likely to have those phrases picked up by AI engines.
When a brand is described the same way on many trusted sites, AI engines will use that view in their answers.
GEO benefits are industry-specific
Some industries find more immediate value in GEO than others.
- Technology and SaaS: A high volume of queries regarding features and technical concepts makes GEO essential for documentation and comparisons.
- Healthcare and Finance: Users frequently ask AI for advice or explanations of complex concepts. Evidence-based, well-cited content in these “Your Money or Your Life” (YMYL) niches captures significant authority.
- Education: Learning-related queries align perfectly with typical AI usage patterns.
- E-commerce: While product pages are cited less often, educational content like buying guides and comparison articles allows brands to associate themselves with expertise at the research stage of the buyer’s journey.
Measuring Performance in a “Zero-Click” World
Traditional metrics like average position are less relevant in GEO. Success must be measured through different methods:
- AI Bot Traffic: Create custom segments to filter traffic from known AI user agents such as ChatGPT-User, PerplexityBot, and Claude-Web.
- Manual Citation Audits: Periodically query AI platforms with core industry questions to see if your brand is cited and in what context.
- Brand Sentiment and Accuracy: Conduct audits to ensure AI platforms are not spreading outdated or inaccurate information about your products.
- Assisted Conversions: Track users who may have discovered the brand via an AI citation and subsequently converted through other channels.
Mistakes to Avoid and Common Pitfalls
Optimizing for generative engines requires moving away from certain SEO habits.
- Assuming Rankings Equal Visibility: Being #1 on Google does not guarantee an AI citation if the content lacks structural elements AI prefers.
- Over-reliance on Visuals: AI engines rarely reference images, charts, or screenshots in text-based chat results; value must be present in the text.
- Content Duplication: Repeating the same answer across multiple pages can confuse LLMs, making it harder for them to detect relevance.
- Unedited AI Content: Generative search engines frequently classify large amounts unedited AI-generated text as low-value.
- Keyword Stuffing: Unlike older SEO methods, RAG systems value conceptual clarity over keyword density.
The GEO Recovery Playbook
If citation frequency drops, a systematic recovery process is necessary.
- Diagnostic Check: Verify content freshness and schema validity using tools like Google’s Rich Results Test.
- Refresh Statistics: Update all numerical data to the most recent figures available.
- Enhance FAQ Sections: Add new questions based on current user trends identified via question research tools.
- Strengthen Citations: Replace broken links or upgrade blog-level citations to academic or primary sources.
- Monitor AI Bot Traffic: Track declines or gains in GA4 over a 60-day window to see if updates are taking effect.
Scaling GEO with Advanced Tools
A specialized toolkit is required for effective large-scale implementation.
- Content and Research: Tools like Frase and Answer The public identifies the specific questions users ask AI platforms and provides templates for “answer-first” content.
- Insights and Strategy: MarketMuse and Surfer AI can highlight content gaps and competitive opportunities.
- Schema Markup: Google’s Rich Results Test and Yoast SEO ensure that article and FAQ schema are correctly implemented, allowing AI engines to categorize data.
- Local Visibility: For local businesses, an optimized Google Business Profile is critical, as engines such as Gemini pull data directly from these profiles for local queries.
How Geo is integrated into white scholars’ digital marketing course
The White Scholars Training Academy in Hyderabad integrates GEO-targeting into its digital marketing course by teaching students how location-based data shapes campaigns. Learners practice using tools like Google Ads and social media platforms to design ads tailored to specific regions, demographics, and cultural contexts.
In the Digital Marketing Course, through hands-on projects, they analyze customer behavior by geography, optimize keywords for local searches, and create region-specific content strategies. This approach helps students understand how businesses reach the right audience at the right place and time.
By applying GEO concepts practically, students gain confidence in crafting impactful, localized campaigns that drive engagement and measurable results.
Final Thoughts
Generative Engine Optimization (GEO) adapts content for AI tools like ChatGPT. Unlike SEO, it focuses on citations rather than clicks. Key strategies include authoritative citations, expert quotes, and high fact density (one statistic per 150-200 words).
Content structure is vital: use an answer-first approach (opening 40-60 words), semantic chunking, and question-format headings. Performance is measured via GA4 AI bot traffic and manual audits.
This approach helps brands future-proof visibility in a zero-click era where AI synthesizes responses directly from trusted sources. Platform-specific tactics vary, but universal principles ensure resilience against algorithm changes.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is GEO replacing traditional SEO?
No, GEO is a complementary practice rather than a replacement; while SEO drives clicks for navigational and transactional searches, GEO targets informational queries where AI engines provide direct answers. A successful digital strategy combines both to improve standard search rankings while ensuring brand visibility within AI-generated summaries and snippets.
2. How long does it take to see results from GEO?
Initial citation wins typically appear within 4 to 8 weeks, though “freshness-focused” engines like Perplexity may cite new content in as little as 1 to 2 weeks. Long-term success builds over 6 to 12 months as your domain accumulates authority signals and AI models establish a “source preference” for your reliable information.
3. Can small businesses effectively compete in GEO?
Yes, because AI platforms value content quality, factual density, and niche relevance over a brand’s overall size. Small businesses can achieve high citation rates by focusing on specific long-tail queries, providing unique industry expertise, and using structured data that makes their content easy for models to interpret.
4. What is the ROI of implementing a GEO strategy?
While AI summaries can cause a 34.5% drop in click-through rates, the ROI of GEO comes from owning the “zero-click” answer and building brand authority. Early data suggests AI-referred visitors often convert at higher rates because the AI has already pre-qualified the content as the most relevant solution to their query.
5. How can I track and measure my GEO performance?
Success is measured by segmenting AI bot traffic (like ChatGPT-User or PerplexityBot) in GA4 and conducting manual audits to see if your brand is cited for core industry questions. You should also monitor “brand sentiment” to ensure AI engines are accurately representing your products and look for increases in assisted conversions and branded search volume.
