How Google Ads Helps Digital Marketing: Where to Start

Table of Contents
Nearly 4,966 companies in India use Google Ads, due to high demand for digital marketing. Let’s explore how Google Ads supports marketing.
Understanding Google Ads
Google Ads stands as a cornerstone of the modern landscape, functioning as a highly sophisticated online advertising platform that empowers businesses to connect with potential clients at the precise moment they are seeking specific solutions.
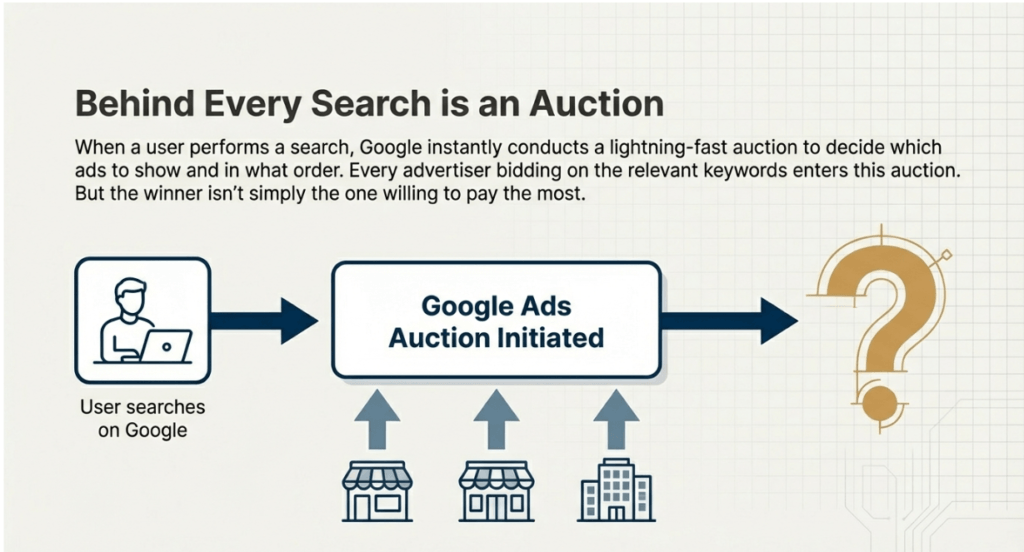
At its core, the platform is designed to facilitate visibility across Google’s extensive network, which includes search result pages, partner websites, and video platforms like YouTube.
Google Ads serves as a primary tool for paid search or search engine marketing (SEM). Unlike organic strategies like SEO, which take time to build authority, Google Ads allows for immediate visibility.
It operates primarily on a pay-per-click (PPC) model, ensuring that advertisers are only charged when a user takes a specific action, like clicking on the advertisement. This makes it a highly efficient component of a strategy, as it aligns marketing spend directly with user engagement.
Demand for Google Ads
The demand for Google Ads comes from its unique ability to reach users who are ready to buy. Since it uses keywords, ads show up for people searching for those terms, making them more likely to take action than those who aren’t actively looking.
Furthermore, demand is driven by the platform’s level of control and precision. Advertisers can set their budgets down to the penny, target specific geographic areas, and even select the devices on which their ads appear.
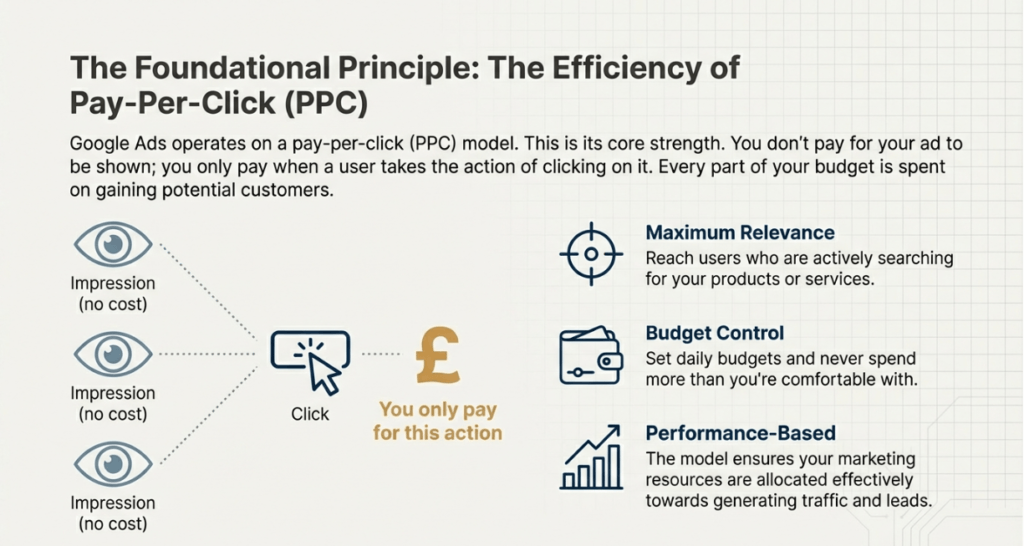
In an era where data-driven decision-making is critical, Google Ads’ real-time performance tracking enables businesses to constantly refine their strategies, resulting in a high return on investment (ROI).
Comprehensive Analysis of Key Google Ads Topics
The following sections provide a detailed explanation of the various facets of Google Ads and associated marketing concepts.
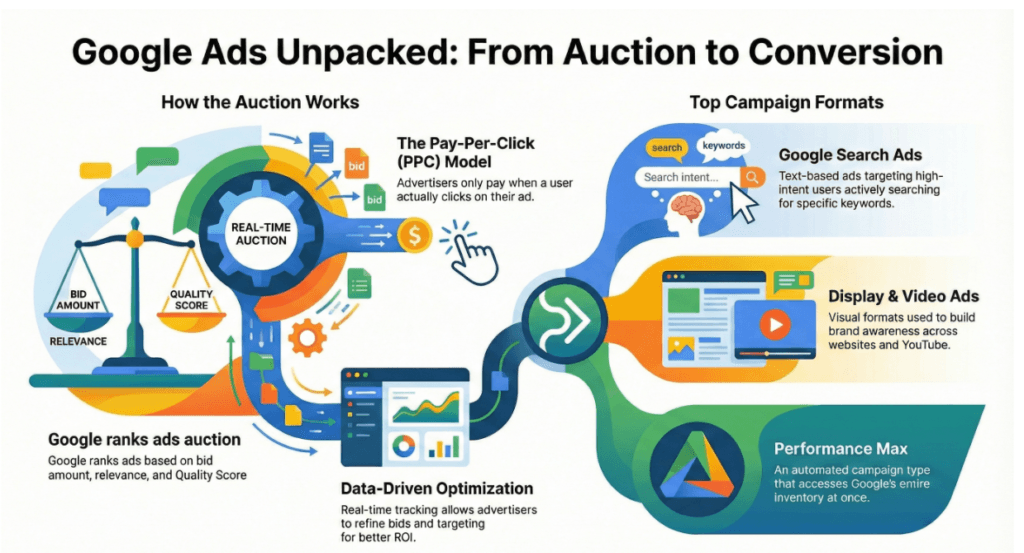
1. The Operational Framework of PPC
Pay-Per-Click (PPC) is the foundational financial model of Google Ads. In this system, advertisers do not pay for the placement of the ad itself but rather for the traffic it generates.
The system utilizes a bidding process where businesses compete for ad space based on specific keywords relevant to their offerings.
2. Categorisation of Ad Formats
Google Ads offers diverse campaign types tailored to different business objectives:
- Text-Based Search Advertisements: These appear directly in the search results. They are composed of headlines and descriptions and are triggered by specific user queries. Their effectiveness lies in capturing “high-intent” shoppers.
- Visual Shopping Campaigns: Managed through the Google Merchant Center, these display product images, prices, and retailer details. They are essential for e-commerce businesses looking to showcase physical inventory.
- The Display Network: These are image-based ads that appear on third-party websites. While they may have lower click-through rates than search ads, they are vital for brand awareness and retargeting.
- Performance Max Solutions: This is a highly automated campaign type that leverages Google’s AI to optimize performance across all of Google’s inventory, including Search, YouTube, and Display, using a single setup.
- Video-Based YouTube Ads: These appear before or during video content. They are particularly useful for storytelling, product education, and building brand recognition through visual engagement.
- Gmail-Specific Ads: These appear in a user’s inbox, mimicking the look of an email. When expanded, they provide a full-page ad experience with links and images.
3. Why the Platform Excels
The effectiveness of Google Ads is attributed to its granular targeting and the PPC model. By reaching users based on browsing history, location, and search intent, it increases the probability of conversion.
Additionally, the platform provides businesses with complete autonomy over their marketing resources, allowing for real-time adjustments based on performance data.
4. The Lifecycle of a Campaign: A Seven-Step Process
To understand how Google Ads functions in practice, one must look at the campaign lifecycle:
- Goal Selection: Defining whether the objective is traffic, sales, or leads.
- Keyword Investigation: Identifying the terms users type into the search engine.
- Ad Grouping: Organizing related keywords into clusters to trigger specific, relevant ads.
- Financial Bidding: Deciding the maximum amount to pay per click and setting daily limits.
- The Auction Mechanism: A real-time process where Google evaluates bids, ad quality, and relevance to determine which ads win the top spots.
- Ad Enhancements: Using “extensions” to add phone numbers, location data, or additional links to an ad.
- Data Analytics: Monitoring clicks, impressions, and conversions to refine future efforts.
5. Critical Metrics and Advanced Concepts
- Quality Score: This is a vital metric that evaluates the relevance of your keywords and the quality of your landing pages. A higher score can actually lead to lower costs and better ad positioning.
- The Auction Process: Every time a search is performed, an auction occurs. Google ranks ads based on the bid amount, the quality of the ad, and the expected impact of ad extensions.
- Retargeting: This involves showing ads to users who have previously visited your website, keeping your brand top-of-mind.
- Programmatic Advertising: An automated method of buying and selling ad space, often used in the Display Network.
- Google Tag Manager is a tool that allows marketers to manage and deploy marketing tags (code snippets) on their websites without having to manually modify the code.
6. Broader Digital Marketing Integration
Here’s a list of several interconnected topics that a professional should master:
- SEO (Search Engine Optimization): Unlike Google Ads, this focuses on organic (unpaid) ranking through meta titles and descriptions.
- Social Media Advertising: Platforms like Facebook Ads offer different demographic targeting options compared to Google’s intent-based search.
- Marketplace PPC: Examples include Amazon PPC, which targets ads specifically at Amazon customers.
- Performance Marketing: This term refers to marketing programs in which advertisers pay only when a specific action is completed.
7. Educational and Professional Development
For those looking to enter this field, it is mandatory to know the importance of structured learning. Digital marketing courses, such as those offered by White Scholars Course in Hyderabad.
How Google ads is explained in White scholar’s Digital Marketing Course
Google Ads is taught as a core component of WhiteScholars Academy’s AI-Powered Certification Course in Hyderabad, following a practical, job-ready framework. The curriculum for classes is intended to take students from basic setup to advanced performance marketing strategies.
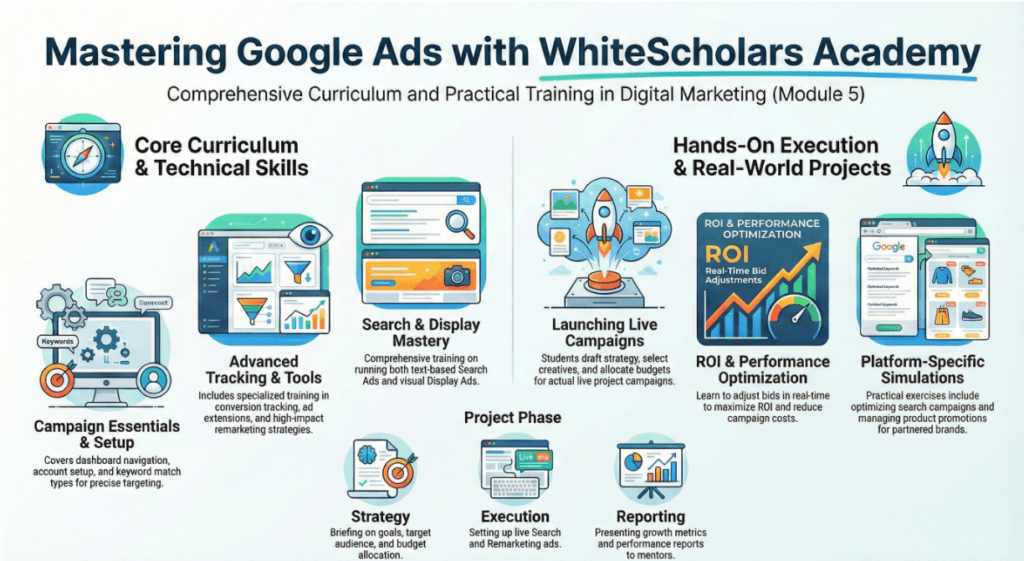
In training, students receive in-depth training on the professional dashboard and technical settings, including:
- Account Setup and Dashboard Review: Learning the interface used by industry professionals.
- Ad Formats: Mastering the creation and execution of search ads and display ads.
- Strategic Features: Understanding keyword match types, the use of extensions, and the implementation of conversion tracking.
- Advanced Tactics: Learning how to re-engage audiences through remarketing ads.
Practical Campaign Execution The training distinguishes itself by requiring students to launch and manage live campaigns for partnered companies. This real-world implementation involves:
- Briefing & Strategy: Analyzing business scenarios to draft tailored marketing plans.
- Decision Making: Students take full responsibility for ad creatives, audience targeting, and budget allocation.
- Ongoing Optimization: Learners monitor results in real time to adjust bids and tweak strategies to maximize ROI and lower campaign costs.
Career Readiness To ensure industry alignment, students compile performance reports and present their strategies to mentors for feedback. Mastery of these tools can lead to various career paths, including roles as PPC specialists, performance marketers, or even starting a agency.
Additional Marketing Skills
Beyond the technical setup of ads, a successful strategy requires
- Lead Generation: Techniques for identifying and cultivating potential customers.
- Link Building: Enhancing SEO authority by acquiring links from other websites.
- Content Marketing: Developing skills to turn readers into customers.
- Buyer Personas: Defining the ideal customer to better target ad copy.
- Email Marketing: Using Substack or traditional email guides to nurture leads.
Google Ads is not a standalone tool but a sophisticated engine that, when integrated with SEO, content strategy, and robust data tracking, forms the backbone of a successful presence. Through its various ad formats, from Search to YouTube, it ensures that a brand remains visible throughout the entire customer journey.
Final Thoughts
Google Ads is an indispensable engine within the digital marketing ecosystem because it provides businesses with immediate visibility to high-intent users at the exact moment they are searching for solutions.
Its primary role is to serve as a versatile lead generation and brand awareness tool that adapts to various stages of the customer journey through formats like Search, Display, and YouTube. By operating on a pay-per-click (PPC) model, it ensures that marketing budgets are utilized efficiently, as advertisers only pay when a user actively engages with an ad.
Furthermore, the platform’s importance lies in its data-driven precision. It enables granular targeting based on search queries, geographic location, and browsing behavior, resulting in highly relevant advertisements to the consumer.
Google Ads complements organic efforts like SEO by providing instant results and actionable performance metrics.
Whether through text-based search or automated Performance Max campaigns, Google Ads gives businesses complete control over their bidding and budget while maximising ROI. Ultimately, mastering this platform is a foundational requirement.
Frequently asked questions
1. What is the basic operational model of Google Ads?
Google Ads operates on a pay-per-click (PPC) model, meaning advertisers only incur costs when users actually click on their ads. The system relies on businesses bidding on specific keywords; Google then uses an automated auction to display relevant ads to users searching for those terms.
2. How does the Google Ads auction process work?
The auction is a dynamic process that determines the ad rank and visibility for each search query. Google evaluates various factors, including the advertiser’s bid, ad quality, and the relevance of the landing page, to decide which ads earn the top positions.
3. What is the significance of a Quality Score?
Quality Score is a diagnostic metric used to evaluate the relevance and performance of your keywords, ads, and landing pages. Maintaining a high score is essential for success, as it typically results in lower cost-per-click (CPC) and superior ad placement on the results page.
4. What types of ad campaigns are available to students?
Businesses can choose from several formats, such as text-heavy Search Ads, visual Shopping Ads, and image-based Display Ads found on third-party sites. Other options include YouTube video ads, Gmail-based messages, and Performance Max campaigns, which automate placements across Google’s entire network.
5. How do you create a Google Ads campaign from scratch?
Setting up a campaign involves selecting a business goal, choosing an ad type, and defining a daily budget. Advertisers must then conduct keyword research, organize ad groups, and create compelling ad copy before launching and tracking the campaign’s performance.
