Inside Generative AI: Tokenization and Embeddings Explained
Table of Contents
This brief guide explains how generative AI understands text using tokenization, embeddings, and vectors to create meaningful, human-like responses.
The machines are no longer just answering questions.
They are writing your emails.
Designing your logos.
Reviewing your code.
And quietly reshaping your career path.
This did not start with hype.
It started with a shock.
One day, AI was a background tool.
The next day, it wrote better text than most humans, in seconds.
If you felt that shift in your gut, you are not imagining it.
Generative AI is different.
And once you understand why, you will never look at software the same way again.
Old AI vs Generative AI
Old AI helped humans decide.
Generative AI helps humans create.
That is why people are paying attention.
What Generative AI Really Is
Most traditional AI systems analyze data.
They classify.
They predict.
They recommend.
Generative AI creates.
It produces:
- Text that sounds human
- Images that never existed
- Code that compiles and runs
- Audio that speaks with emotion
- Video that feels directed, not rendered
In simple terms:
Generative AI learns patterns so deeply that it can produce new content that fits those patterns.
It does not copy.
It generates.
That single difference changes everything.
At the core of most modern Generative AI systems is a Large Language Model (LLM).
What is an LLM?
LLM = Large Language Model
Examples:
- GPT (OpenAI)
- Gemini (Google)
Key Idea
An LLM does not understand language like humans. Instead, it:
- Converts text into numbers
- Learns statistical patterns
- Predicts the next most likely token
Tokenization
What is Tokenization?
Text → Tokens
Tokenization is the process of breaking text into smaller units called tokens.
Why Tokenization?
- Neural networks cannot process raw text
- They work only with numbers
Each token maps to a unique numeric ID.
User Request → Model Flow
- User sends a query
- Text is tokenized
- Tokens are converted into numerical representations
- Model processes the numbers using neural networks
- Model generates output tokens
- Tokens are converted back into readable text
Embeddings
What are Embeddings?
Embeddings are numerical vectors that represent the meaning of words, sentences, or documents.
Meaning → Vector Space
- Text → Vector (array of numbers)
- Similar meanings → vectors close together
Vector Databases
A Vector Database stores embeddings and allows search by meaning.
How Vector Search Works
- Convert user query → embedding
- Search vector DB for nearest vectors
- Retrieve most relevant documents
Generative AI Architecture and Workflow
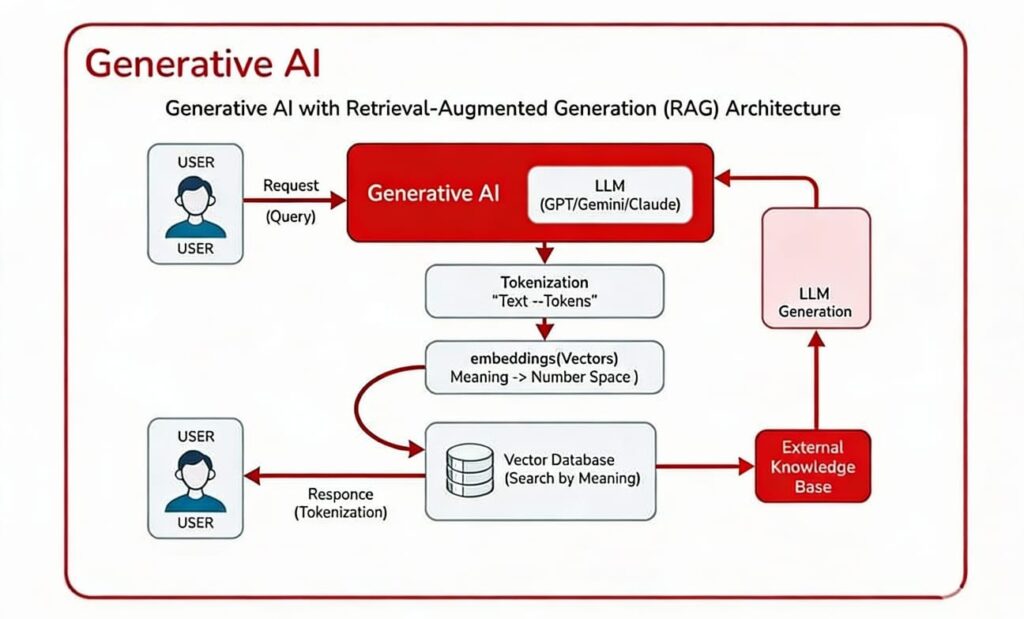
- The “Generative AI” aspect is fed into “LLM”s such as “GPT/Gemini/Claude”.
- The overall workflow begins with a user “Request (Query)”.
This input goes into a Large Language Model (LLM) → The model then Tokenizes → turns the data into an “Embedding (Vectors)” → That information is stored in a Vector Database that uses “Search by Meaning” to find relevant information → And then is sent back to the User with a “Response (Tokenization)”.
- An “External Knowledge Base” can connect to the Vector Database to help with the processing.
Data Science Course in Hyderabad at WhiteScholars
For graduates willing to go deeper into Generative AI and machine learning algorithms, a data science course in Hyderabad through WhiteScholars can be the next step after foundational analytics skills. This typically adds supervised and unsupervised learning, model evaluation, feature engineering, and possibly deep learning basics, framed around real-world problems.
With this path you can:
- Work toward roles like junior data scientist, ML engineer trainee, or applied AI analyst, which require both coding skills and understanding of business use-cases.
- Position yourself for long-term growth, as data science remains one of the highest-paying and fastest-growing segments in the engineering job market in India through 2026 and beyond.
Glossary of Key Terms
- Tokenization: The process of breaking down text into smaller units (tokens), such as words or sub-words, that can be processed by an LLM.
- Tokens: The individual units of text resulting from the tokenization process (e.g., “the,” “cat,” “sat”).
- Vector Embedding: A numerical representation of a word, phrase, or other data type in a multi-dimensional space, capturing its semantic meaning and relationships to other concepts.
- Vector Database: A database specifically designed for storing and searching vector embeddings, enabling efficient similarity searches based on semantic meaning.
- Embedding Service: The component responsible for transforming raw data into vector embeddings.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is tokenisation and why is it important ?
Tokenisation is the process of breaking down a text input into smaller units called tokens. These tokens can be words or sub-words tokenisation is used because they can’t directly process raw text. Instead, they work with numerical representations of these tokens. This process enables the model to understand the structure and meaning of the input.
What types of data can be used to create vector embeddings?
Vector embeddings are not limited to text. They can be created from images, audio, and video data. For each type of data, it’s necessary to have a service which can create appropriate embedding from the raw data, e.g. an image recognition algorithm or a voice-to-text converter. This allows for more sophisticated AI models which understand different types of information.
What is a vector database and what is its purpose?
A vector database is a specialised database designed to store and efficiently search through vector embeddings. Unlike traditional databases which are optimised for exact matches, vector databases are designed to find the closest matches based on the similarity of the vectors. This is critical for LLMs, allowing them to retrieve relevant information based on the meaning of the query, rather than just matching keywords.
What is Generative AI ?
A type of artificial intelligence that can generate new content, such as text, images, or music.
What is LLM (Large Language Model) ?
A type of AI model trained on vast amounts of text data, capable of understanding and generating human-like text.
What is GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) ?
A specific architecture of LLM developed by OpenAI known for its ability to generate coherent and contextually relevant text.
