Master Data Science: Secure Your Career in the Age of AI
Table of Contents
In an uncertain AI age, select a lasting path. Discover how data science can secure your career, enhance it with generative AI, and forecast the demand in 2026.
What is data science, and why is there a shift?
Data science is fundamentally a technical role that requires coding and analytical skills to convert raw data into a structured, presentable format that can help a business grow.
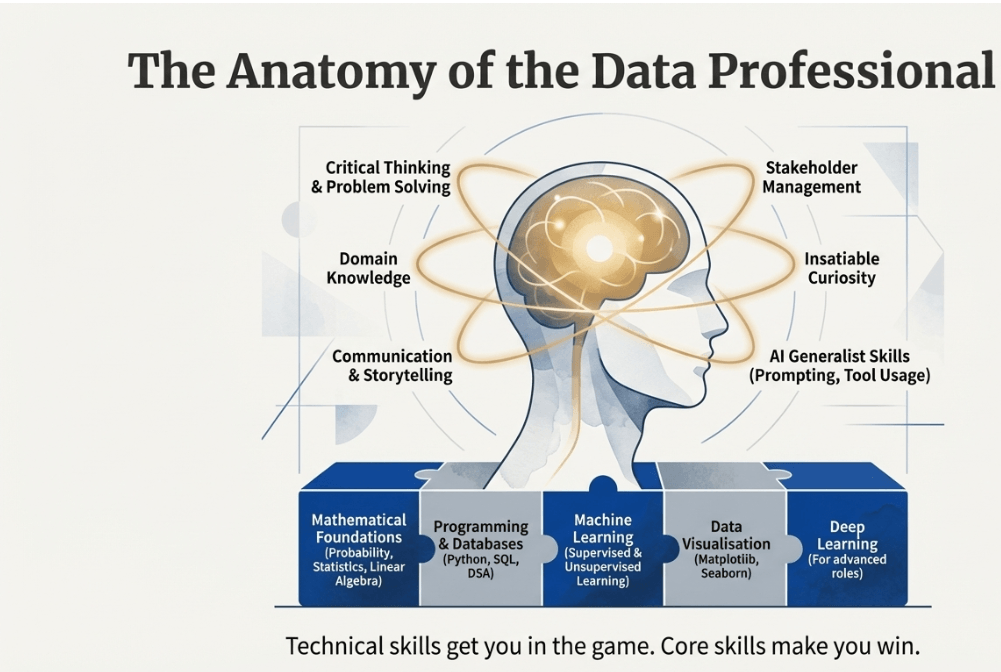
The role of data science is defined by the intersection of three specific fields: mathematics, programming, and business.
These three components function as follows:
- Math: This is the essential foundation for creating and comprehending models. Linear algebra for machine learning and deep learning calculations, probability to determine the likelihood of outcomes, statistics to study consumer patterns and sales, and calculus to minimise errors during model training are all important topics.
- Programming is the technical toolkit used to manage data. While R was once popular, Python is now used in 90% of corporate cases due to its simple syntax and powerful libraries such as NumPy and Pandas for data manipulation, as well as Matplotlib and Seaborn for visualisation.
- Business Aspect (Domain Expertise): This entails understanding how to apply data insights to help a company grow. It is considered a core skill due to technical work that includes data visualisation tools such as Power BI, Tableau, and others.
Combining these fields is critical because, while AI can help with the “mundane” tasks of programming and mathematical calculations, it takes a human with domain expertise to ensure that the results are not only numerically convincing but also logically sound for a given business context.
The sheer volume of data produced is driving the shift towards data science; interestingly, 90% of the world’s data was created in the last two years alone. Because most of this data is raw, there is a huge demand for professionals who can interpret, analyse, and structure it to make strategic decisions.
The 2026 Outlook: Statistics and Growth
As we look towards 2026 and beyond, the demand for data professionals is expected to skyrocket:
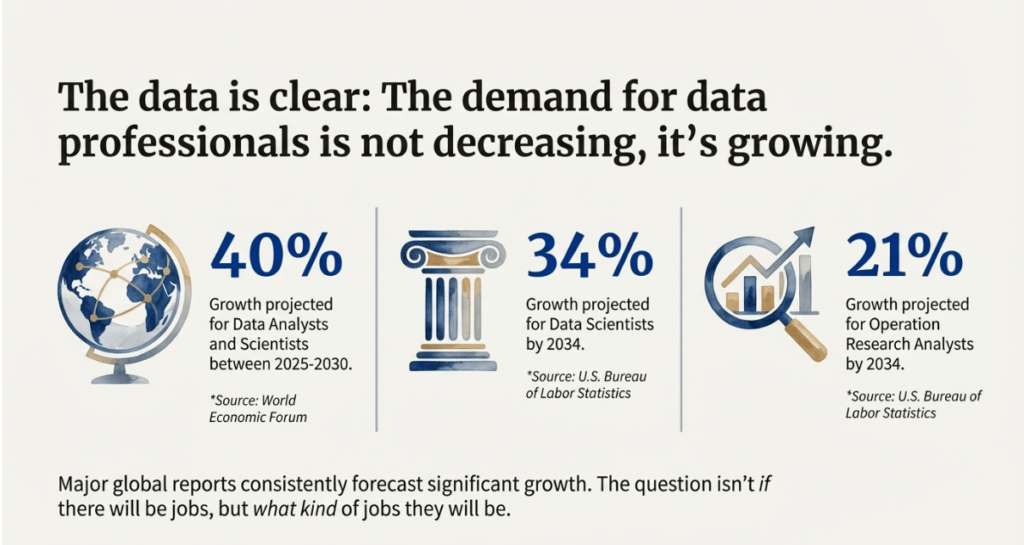
- 40% Growth Rate: The World Economic Forum predicts that jobs for data analysts and scientists will increase by 40% between 2025 and 2030.
- Sector-Specific Growth: According to the U.S. Bureau of Labour Statistics, demand for data scientists will increase by 34% by 2034, while demand for operation research analysts will increase by 21%.
- Hiring Trends: While some product companies prioritise upskilling current employees, startups and service companies continue to actively seek new employees for these positions.
Future-Proofing Your Career: Why AI Won’t Replace Data Science
Unlike many other careers that are being completely automated, data science is being augmented rather than replaced by the AI revolution.
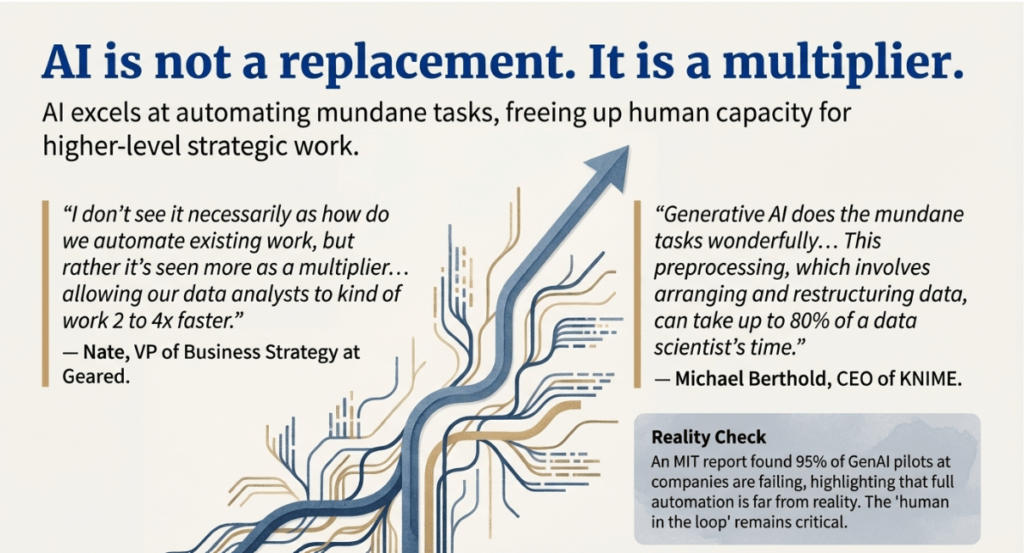
- The “Human in the Loop”: Experts see AI as a multiplier, allowing analysts to work two to four times faster. However, the principle of “bad data in, bad data out” remains in effect; humans are required to verify results and manage data pipelines.
- Deriving New Insights: While Large Language Models (LLMs) excel at processing existing knowledge, they fall short when it comes to generating entirely new insights or knowledge. Human domain expertise provides business value by recognising when a numerically convincing result is logically incorrect.
- Critical Thinking: Artificial intelligence can hallucinate, producing plausible but illogical results. A data scientist’s ability to use critical thinking to question these outputs is more important than ever.
Skills required to become a data scientist
To succeed in this field in 2026, you’ll need a mix of technical and “soft” skills:
- Mathematics: Strong foundations in linear algebra (for machine learning models), probability (for likelihood-based predictions), statistics (descriptive and inferential), and calculus (for model error minimisation).
- Programming & Tools: Python proficiency is required due to its extensive libraries, including NumPy and Pandas for data manipulation and Matplotlib or Seaborn for visualisations.
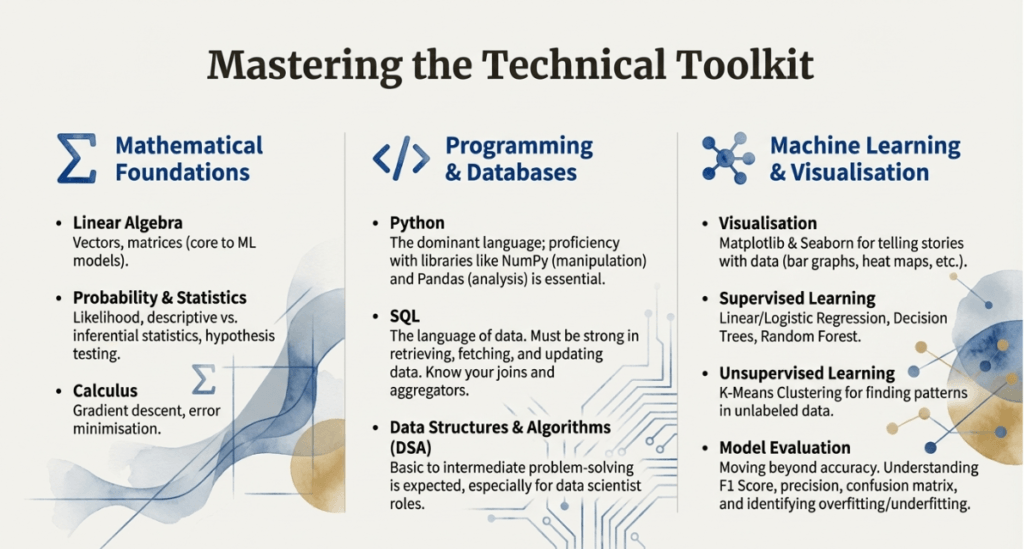
- Databases: Strong SQL skills are required to retrieve and update data from databases.
- Knowledge of supervised and unsupervised learning (e.g., regression, decision trees, K-means) as well as deep learning frameworks such as TensorFlow or PyTorch.
- In addition to coding, you must be proficient in problem solving, stakeholder management, storytelling, and domain expertise.
Generative AI: Strengthening the Data Scientist
Generative AI acts as a customisable super assistant, significantly reducing the time spent on repetitive and foundational tasks, which can account for up to 80% of a data scientist’s workload. By automating these routine elements, technology serves as a productivity multiplier, allowing professionals to work twice to four times faster than before.
Automating Coding and Technical Tasks
One of the most immediate ways generative AI can help is by handling technical “boilerplate” work and syntax requirements.
- Syntax Support: Instead of memorising complex syntax or searching through Google, data scientists can use Large Language Models (LLMs) to generate Excel formulas or Power BI DAX code in seconds.
- Code Embeddings: It improves code embeddings, making it easier for computers to process and understand the relationships between various code segments.
- Module Configuration: It allows you to configure complex modules and create building blocks for various generative AI codes, which complements existing analytics platforms.
Data Preparation and Preprocessing
Generative AI has a significant impact on preprocessing, also known as “plumbing” in data science.
- ETL Workflows: AI handles the mundane details of the data science workflow, specifically Extracting, Transforming, and Loading (ETL).
- Data Quality and Matching: It can compare datasets to see how they fit together and help establish better data quality processes.
- Standardised Tasks: Routine tasks can be easily offloaded to AI, freeing up human professionals to focus on complex puzzles and unique insights that AI cannot derive on its own.
Research and Business Insight
AI automates the initial stages of project discovery and learning.
- Rapid Research: When trying to understand a new business process or researching Key Performance Indicators (KPIs), AI provides quick summaries and research findings.
- Upskilling Literacy: For those new to the field, AI chat assistants can “upskill data literacy” by explaining Visual Basic (VB) code or identifying available functions in tools like Excel.
- Dashboarding: AI tools can now partially or completely automate the creation of technical dashboards, which was previously a core manual task for “Data Analyst 1.0” roles.
The Role of the “Human in the Loop”
While AI handles these routine tasks, the sources emphasise that it does not eliminate the need for humans. AI is prone to hallucinations, producing plausible but illogical results, necessitating critical thinking by a data scientist to verify every output. Even if the AI’s numerical output is convincing, humans are still required to manage the data pipes and ensure that the final results are logically sound.
White Scholars Training Institute In Hyderabad
WhiteScholars Academy offers a specialised data science and generative AI certification program in Hyderabad, available through online, offline, and hybrid learning formats. The curriculum provides over 180 hours of instruction covering essential technical subjects such as Python, machine learning, SQL, and deep learning.
Students gain hands-on experience by completing several real-world projects and capstone assignments to create a professional portfolio. Aside from technical training, the institute offers comprehensive career support, such as mock interviews, resume building, and guaranteed interview opportunities through a network of hiring partners.
This beginner-friendly course aims to bridge the skills gap for new graduates and working professionals seeking high-growth opportunities in the technology sector. Through collaborations with industry leaders and major corporations, the academy ensures that its graduates have job-ready skills and internationally recognised certification.
Responsibility And Role Of A Data Scientist
A data scientist’s responsibilities and roles in a company are multifaceted, ranging from technical “plumbing” to high-level strategic decision-making.
1. Data Preparation and Management
A significant portion of the job entails Extracting, Transforming, and Loading (ETL) data. Data scientists are in charge of preprocessing, which includes organising and restructuring data to ensure it is of high quality and correctly matched. This preparation can take up to 80% of a professional’s time, but it is critical to ensuring that the data is ready for analysis.
2. Building Predictive Models
Data scientists use mathematical foundations like linear algebra, probability, and calculus to create and train machine learning and deep learning models.
- They create algorithms for applications such as face recognition, spam filtering, and recommendation systems.
- They are in charge of model tuning and testing to reduce errors and improve accuracy through metrics such as the F1 score and precision.
3. Driving Business Growth
The primary goal of the position is to use data to help a business grow. Data scientists serve as strategic partners, looking beyond the numbers to deliver business value. They identify patterns and investigate anomalies to determine “why” certain trends occur, such as studying consumer behaviour or predicting whether a discount will actually increase sales.
4. Visualisation and storytelling
Because senior management and CEOs may not understand complex code, a data scientist must be able to visually present findings. They use tools to create bar graphs, pie charts, and heat maps that make data “visually appealing” and understandable to those making final business decisions. Their role is to use data to tell a story that will result in meaningful change.
5. Stakeholder Management
A data scientist must manage the expectations of a variety of stakeholders, including business managers and engineers. This requires effective communication and domain expertise, as well as a thorough understanding of the specific industry to determine when an analysis logically fits the business context.
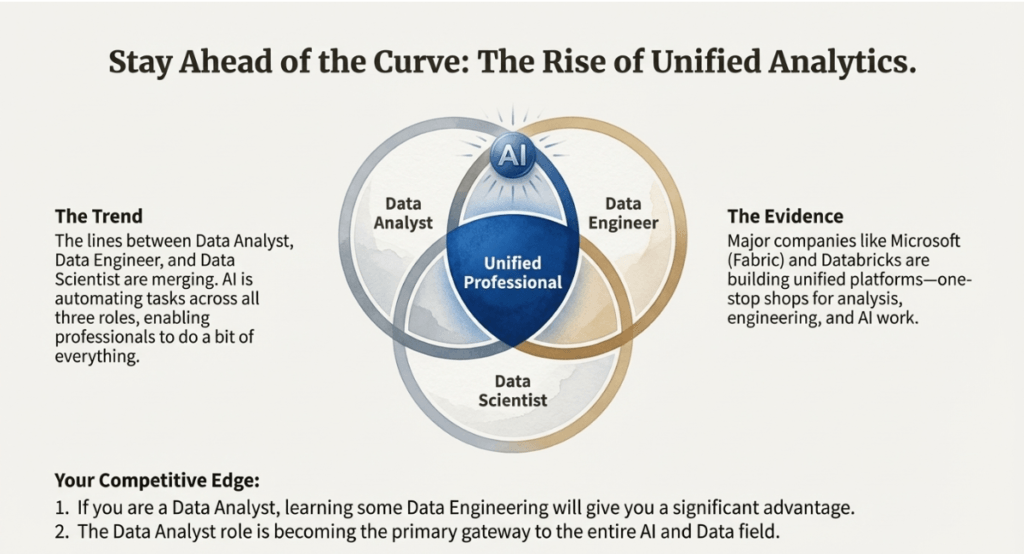
Diverse Roles in the Data Science & Generative AI Market
The incorporation of generative AI is causing a shift towards unified analytics, in which previously distinct roles are beginning to merge. The key roles include:
Data Scientist: Builds machine learning models and deep learning architectures from unstructured data such as images and audio.
Data analysts serve as strategic partners, leveraging AI tools to provide business value and storytelling. They help businesses make data-driven decisions.
AI Engineer: A position that focuses on the deployment and management of AI models, usually obtained after gaining experience in data analysis.
Data Engineer: Concentrates on the “pipes” or infrastructure of data; this role is increasingly merging with analysis to create unified analytics professionals.
ML Engineer: Specialised in supervised and unsupervised learning models, as well as model tuning.
Final Thoughts: Data Science vs. Technical Jobs
Choosing data science is more secure than selecting purely technical jobs. Those who focus solely on technical tools face a bleak future, as AI can already automate those tasks.
The primary advantages of generative AI in this field are that it eliminates repetitive tasks and acts as a bridge to more advanced roles like AI engineering. Combining technical expertise with curiosity and business acumen ensures that you are more than just a tool user, but also a strategic partner that AI cannot compete with.
To succeed, aspiring professionals must establish online credibility and adapt to unified analytics, in which data analysis, engineering, and AI roles merge. Ultimately, the career remains a strong gateway into the broader technology sector for those committed to continuous upskilling.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. Will artificial intelligence (AI) replace data scientists and analysts in 2026?
AI functions more as a “multiplier” than a replacement, allowing professionals to work two to four times faster. While it automates routine tasks, humans are required to manage data “pipes” and ensure that results are logically correct. Large Language Models (LLMs) frequently “fall flat on their face” when tasked with generating entirely new insights or unique business knowledge. As a result, having a “human in the loop” is still required to detect illogical outcomes or AI hallucinations.
2. What essential skills are required to become a data scientist?
Math, programming, and business knowledge are all required for success in this field. Linear algebra is essential for machine learning, and statistics is used to study consumer patterns. Python is the primary programming language used for data manipulation, whereas SQL is required for database management. To make a real difference in business, you must master “soft” skills like storytelling, domain expertise, and curiosity in addition to technical tools.
3. What is the expected job growth for these positions?
The demand for data professionals is expected to skyrocket, with the World Economic Forum projecting a 40% increase between 2025 and 2030. The United States Bureau of Labour Statistics predicts a 34% increase in the number of data scientists by 2034. While large product companies focus on upskilling their existing employees, startups and service-based businesses continue to actively hire new employees. This increase is driven by the fact that 90% of the world’s data was created in the last two years.
4. How can Generative AI help wx“`ith daily data science tasks?
Generative AI functions as a “super assistant,” handling mundane, routine tasks that can take up to 80% of a scientist’s time. It automates the “Extract, Transform, and Load” (ETL) process and helps you write complex syntax for Excel or Power BI. It also helps to match datasets and improves code embeddings, resulting in better data quality processes. By offloading these “boring” parts of the workflow, professionals can concentrate their efforts on solving complex puzzles and discovering novel insights.
5. What distinguishes WhiteScholars Data Science training from other institutes?
WhiteScholars offers 100% placement assistance and guarantees interview opportunities based on student performance and project completion. Students have lifetime access to all course materials and can earn recognised certifications from Nasscom and Microsoft. Choosing this course is like getting a backstage pass to the tech industry, as it provides the specific tools and network required to transition into a data career.
